Category filter
Script to configure network share on Windows devices
This article explains how to use a script to configure network share on Windows devices.
Network shares on Windows devices allow multiple users on the same network to access and collaborate on files and folders. Creating a network share lets users easily access and share documents, media files, and other resources without physically transferring files between computers. IT administrators can use PowerShell scripts to configure or remove network share on Windows devices and even map a Windows-accessible network drive to a network share. You can now remotely deploy these scripts to multiple endpoints using the Execute Custom Script action of Hexnode UEM.
Configure network share
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
Invoke-CimMethod -ClassName Win32_Share -MethodName Create -Arguments @{ Path = 'Enter the folder path' Name = 'Enter the folder name' Type = [uint32]0 #Disk Drive MaximumAllowed = [uint32]25 Description = 'configure network share with the temp folder' } |
The Invoke-CimMethod cmdlet is used to call the Create method of the Win32_Share class which creates the network share. We define the necessary parameters (Path, Name, Type, MaximumAllowed, and Description) for the share as Arguments. Enter the desired name of your network share (Name) and the local folder path you want to share on the network (Path). This folder will become the contents of the network share.
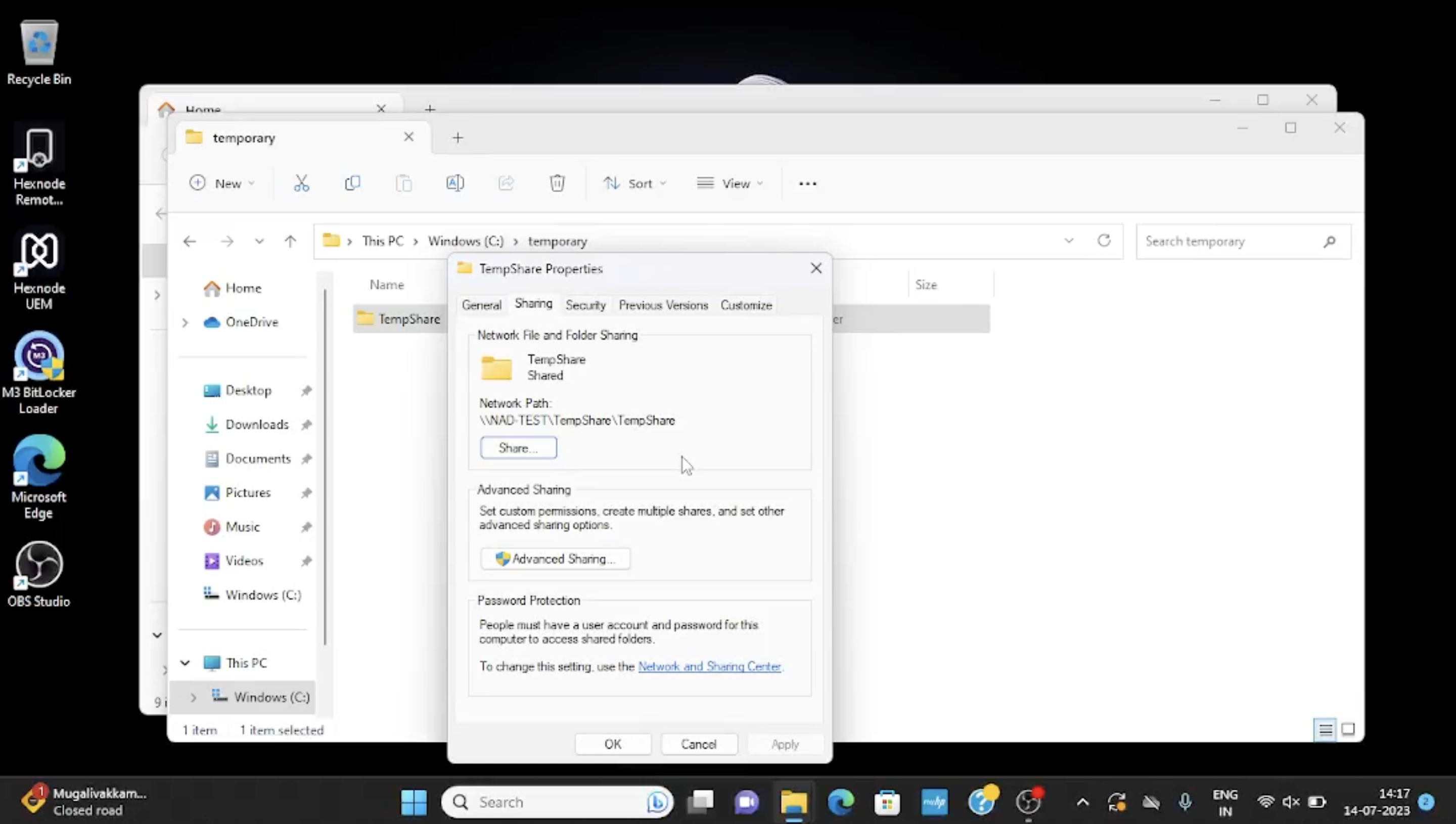
For example, to configure network share with the folder TempShare stored in the file path “C:\temporary”:
Invoke-CimMethod -ClassName Win32_Share -MethodName Create -Arguments @{
Path = 'C:\temporary'
Name = 'TempShare'
Type = [uint32]0 #Disk Drive
MaximumAllowed = [uint32]25
Description = 'configure network share with the temp folder'
}
After running the script, the specified folder will be shared on the network with the assigned share name. Other users on the network will be able to access the contents of this folder using the UNC path: \\ComputerName\SharedFolder, where ComputerName is the name of the computer where the share is created and SharedFolder is the share name you specified in the script.
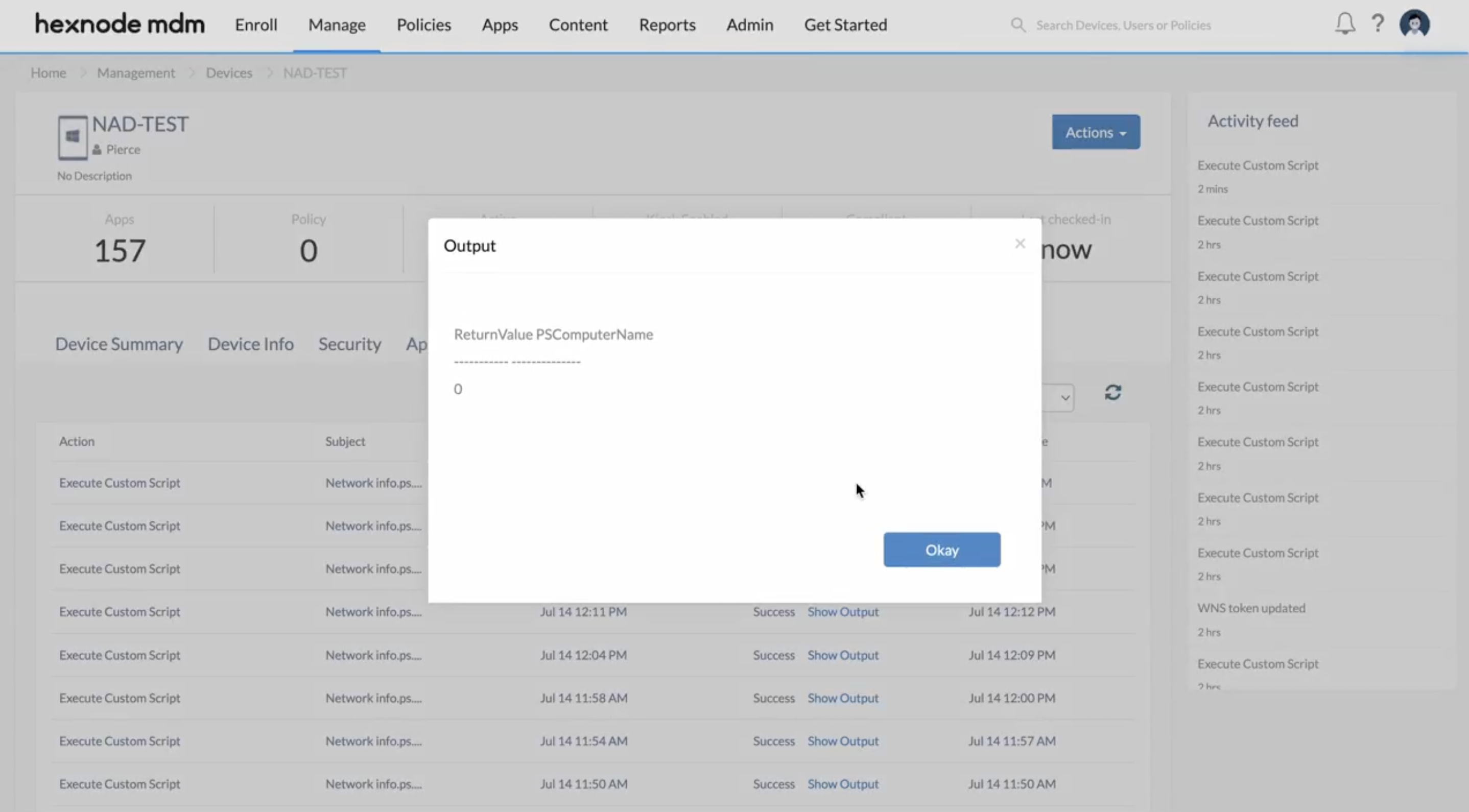
You can verify the execution status of the script to configure network share from the device’s Action History tab.
Remove a network share
|
1 |
$wql = 'SELECT * from Win32_Share WHERE Name="Enter the name of network share"' Invoke-CimMethod -MethodName Delete -Query $wql |
For removing the network share, we first retrieve the specific instance to be removed by specifying the name of the network share in the above script. Invoke-CimMethod cmdlet then uses the Delete method to remove the network share.
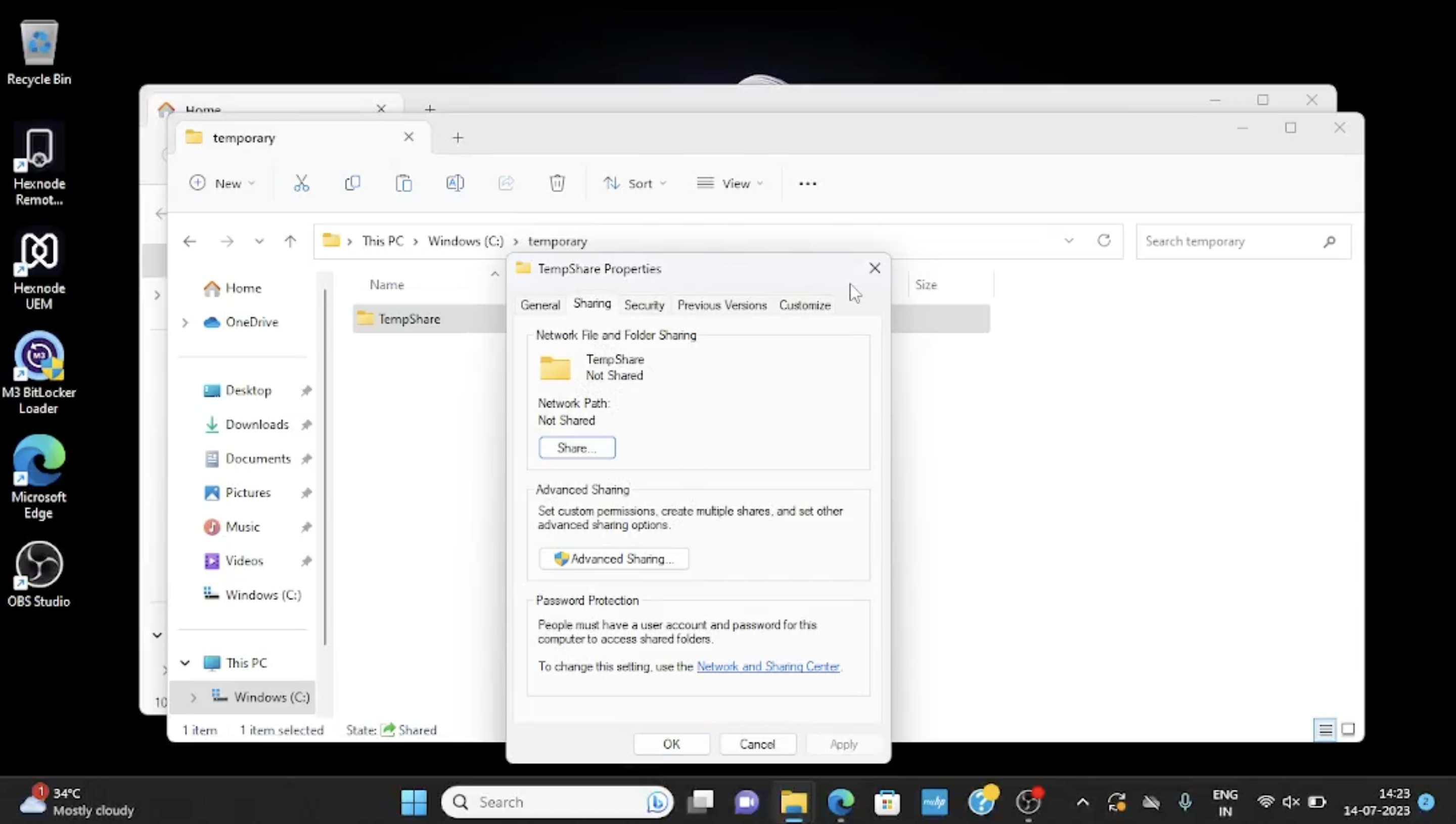
E.g., $rem = 'SELECT * from Win32_Share WHERE Name="TempShare"' Invoke-CimMethod -MethodName Delete -Query $rem
The example given removes the share named TempShare.
Map network drive
|
1 |
New-PSDrive -Persist -Name "X" -PSProvider "FileSystem" -Root "\\ComputerName\SharedFolder" |
The New-PSDrive cmdlet creates a network drive mapped to a network share. Specify the driver letter you want to assign to the mapped drive (Name) and UNC path of the network share you want to map (Root). Specifying the value FileSystem for the PSProvider parameter indicates that the drive is being mapped to a filesystem location. The Persist parameter ensures that the mapped drive persists across PowerShell sessions.
To give an example, the command below creates a mapped network drive with driver letter X and network path \\NAD-TEST\TempShare\TempShare:
New-PSDrive -Persist -Name "X" -PSProvider "FileSystem" -Root \\NAD-TEST\TempShare\TempShare
Once a network drive is mapped, users can access the shared files and folders directly from file explorers, file dialogs, and any other applications without having to remember or type the long UNC (Universal Naming Convention) paths.