Category filter
Script to add secure token to users on macOS devices
As part of APFS encryption on macOS, Secure Token was implemented to carry out crucial cryptographic tasks. For instance, secure tokens are necessary for enabling FileVault disk encryption, executing kernel and system extensions (KEXTS) and mandating software upgrades. Users cannot execute any crucial actions on a macOS device if they do not have a secure token added to their account. However, the secure token is not automatically granted to accounts created via command-line tools and Active Directory Mobile Accounts. With Hexnode, IT admins can easily add the secure token to any user account using the Execute custom script action.
Scripting Language – Bash
File extension – .sh
Add Secure token
Execute the script below to add a secure token for a user account by passing the arguments in the following order to replace $1 $2 $3 $4: AdminAccountName AdminPassword UserPassword UserAccountName.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 |
#!/bin/sh # script parameter: "SecureToken Admin Username" # A local administrator account with SecureToken access. secureTokenAdmin="${1}" # Need a default password value so the initial logic loops will properly fail when validating passwords. UserAccount=${4} macOSVersionMajor=$(/usr/bin/sw_vers -productVersion | /usr/bin/awk -F . '{print $1}') macOSVersionMinor=$(/usr/bin/sw_vers -productVersion | /usr/bin/awk -F . '{print $2}') macOSVersionBuild=$(/usr/bin/sw_vers -productVersion | /usr/bin/awk -F . '{print $3}') # Exits if macOS version predates the use of SecureToken functionality. check_macos_version () { # Exit if macOS < 10. if [ "$macOSVersionMajor" -lt 10 ]; then echo "macOS version ${macOSVersionMajor} predates the use of SecureToken functionality, no action required." exit 0 # Exit if macOS 10 < 10.13.4. elif [ "$macOSVersionMajor" -eq 10 ]; then if [ "$macOSVersionMinor" -lt 13 ]; then echo "macOS version ${macOSVersionMajor}.${macOSVersionMinor} predates the use of SecureToken functionality, no action required." exit 0 elif [ "$macOSVersionMinor" -eq 13 ] && [ "$macOSVersionBuild" -lt 4 ]; then echo "macOS version ${macOSVersionMajor}.${macOSVersionMinor}.${macOSVersionBuild} predates the use of SecureToken functionality, no action required." exit 0 fi fi } # Exits if $UserAccount already has SecureToken. check_securetoken_user () { if /usr/sbin/sysadminctl -secureTokenStatus "$UserAccount" 2>&1 | /usr/bin/grep -q "ENABLED"; then echo "${UserAccount} already has a SecureToken. No action required." exit 0 fi } # Exits with error if $secureTokenAdmin does not have SecureToken # (unless running macOS 10.15 or later, in which case exit with explanation). check_securetoken_admin () { if /usr/sbin/sysadminctl -secureTokenStatus "$secureTokenAdmin" 2>&1 | /usr/bin/grep -q "DISABLED" ; then if [ "$macOSVersionMajor" -gt 10 ] || [ "$macOSVersionMajor" -eq 10 ] && [ "$macOSVersionMinor" -gt 14 ]; then echo "⚠️ Neither ${secureTokenAdmin} nor ${UserAccount} has a SecureToken, but in macOS 10.15 or later, a SecureToken is automatically granted to the first user to enable FileVault (if no other users have SecureToken), so this may not be necessary. Try enabling FileVault for ${UserAccount}. If that fails, see what other user on the system has SecureToken, and use its credentials to grant SecureToken to ${UserAccount}." exit 0 else echo "❌ ERROR: ${secureTokenAdmin} does not have a valid SecureToken, unable to proceed. Please update to another admin user with SecureToken." exit 1 fi else echo "✅ Verified ${secureTokenAdmin} has SecureToken." fi } # Adds SecureToken to target user. securetoken_add () { /usr/sbin/sysadminctl \ -adminUser "$1" \ -adminPassword "$2" \ -secureTokenOn "$3" \ -password "$4" # Verify successful SecureToken add. secureTokenCheck=$(/usr/sbin/sysadminctl -secureTokenStatus "${3}" 2>&1) if echo "$secureTokenCheck" | /usr/bin/grep -q "DISABLED"; then echo "❌ ERROR: Failed to add SecureToken to ${3}. Please rerun policy; if issue persists, a manual SecureToken add will be required to continue." exit 126 elif echo "$secureTokenCheck" | /usr/bin/grep -q "ENABLED"; then echo "Successfully added SecureToken to ${3}." else echo "❌ ERROR: Unexpected result, unable to proceed. Please rerun policy; if issue persists, a manual SecureToken add will be required to continue." exit 1 fi } ########## main process ########## # Check script prerequisites. check_macos_version check_securetoken_user check_securetoken_admin # Add SecureToken to $UserAccount. secureTokenAdminPass="${2}" UserPass="${3}" # Add SecureToken using provided credentials. securetoken_add "$secureTokenAdmin" "$secureTokenAdminPass" "$UserAccount" "$UserPass" |
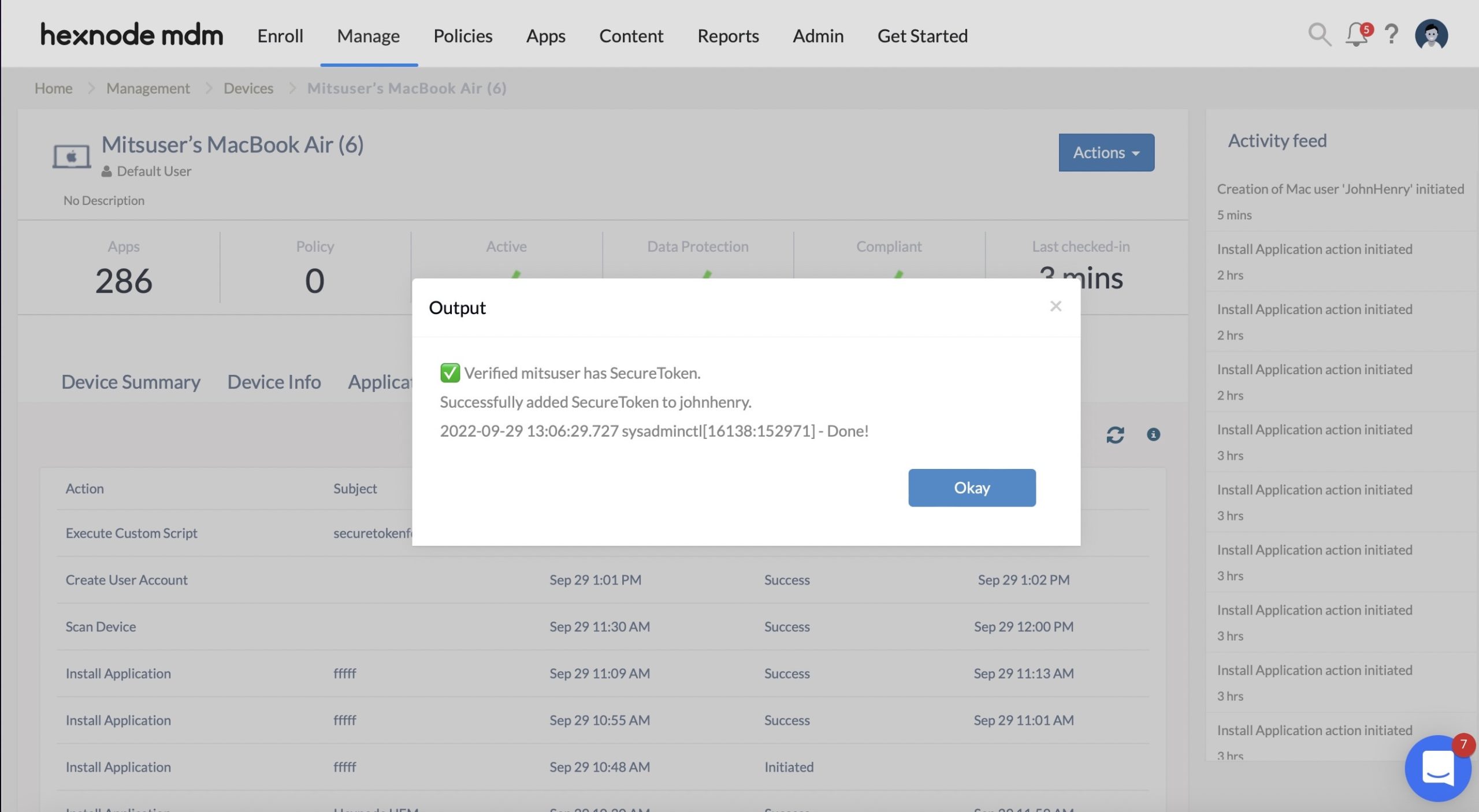
Once the script is executed successfully, you can view a similar output as the following from the Action History tab: