Category filter
PowerShell script to get volume information from Windows devices
Managing storage volume on Windows devices in an organization is crucial for resource utilization. Fetching information about storage volumes like health status, size used, etc., facilitates efficient resource monitoring with the help of a detailed overview of the device’s storage. IT administrators can use the PowerShell script to get volume information on Windows devices. With Hexnode’s Execute Custom Script remote action, IT admins can execute the PowerShell script to get the information about volume on Windows devices.
PowerShell script fetch information of all volumes
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
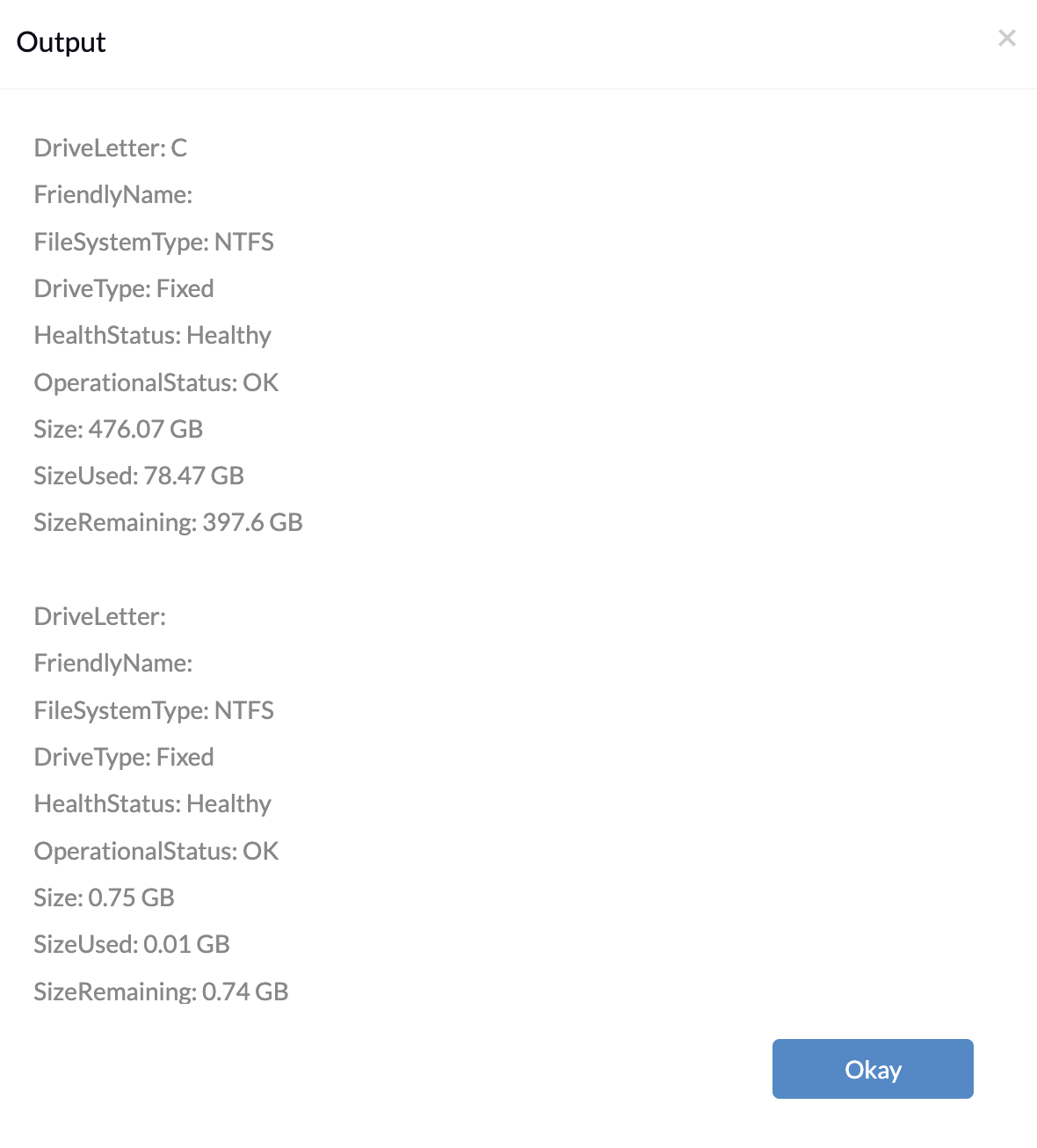
# Get information about all volumes on the computer $volumeInfo = Get-Volume # Output volume information line by line $volumeInfo | ForEach-Object { $sizeGB = [math]::Round(($_.Size / 1GB), 2) $sizeRemainingGB = [math]::Round(($_.SizeRemaining / 1GB), 2) $sizeUsedGB = $sizeGB - $sizeRemainingGB Write-Output "DriveLetter: $($_.DriveLetter)" Write-Output "FriendlyName: $($_.FriendlyName)" Write-Output "FileSystemType: $($_.FileSystemType)" Write-Output "DriveType: $($_.DriveType)" Write-Output "HealthStatus: $($_.HealthStatus)" Write-Output "OperationalStatus: $($_.OperationalStatus)" Write-Output "Size: $sizeGB GB" Write-Output "SizeUsed: $sizeUsedGB GB" Write-Output "SizeRemaining: $sizeRemainingGB GB" Write-Output "" } |
The above PowerShell script uses the Get-Volume command to fetch the information on all the volumes present on the device.
DriveLetter: The letter assigned to the volume used as a reference for accessing the volume within the Windows operating system.
FriendlyName: Friendly name of the volume if there is any. If there is no name set it will display the output as empty.
FileSystemType: The type of file system used on the volume determines how data is stored, organized, and accessed. (e.g., NTFS-New Technology File System, FAT32-File Allocation Table 32, and exFAT-Extended File Allocation Table).
DriveType: This indicates the type of drive the volume is associated with. For example, “Fixed” drives refer to internal hard disk drives, while “Removable” drives include external USB drives.
HealthStatus: Provides information about the overall health condition of the volume, indicating whether any issues or errors have been detected.
OperationalStatus: The operational status of the volume, such as whether it’s online or offline.
Size: Describes the total volume capacity of the device.
SizeUsed: Amount of the size used in the volume.
SizeRemaining: Amount of free space in the volume.
PowerShell script get information of specific volume on Windows devices
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 |
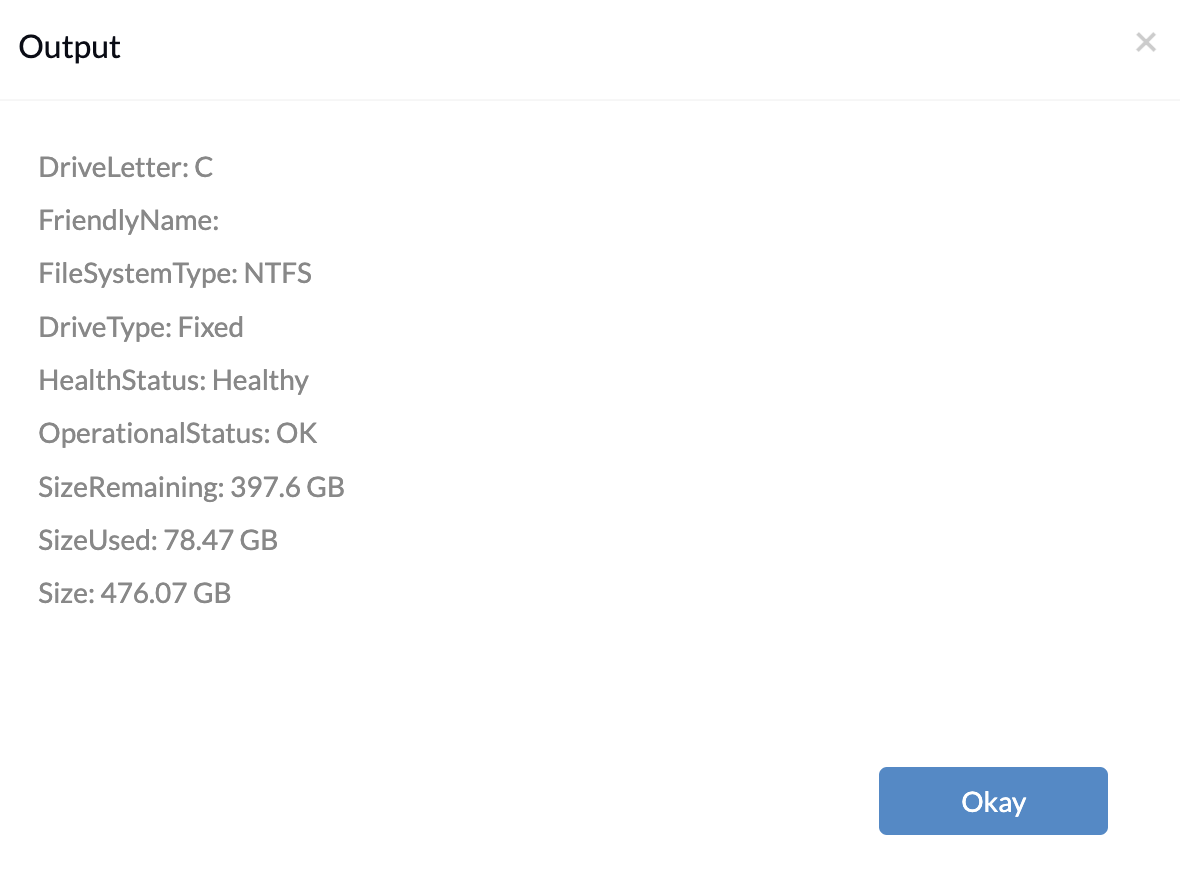
# Define parameter param ( [char[]]$DriveLetter = 'C' ) # Get information about volume with specified drive letter $volumeInfo = Get-Volume -DriveLetter $DriveLetter # Output volume information line by line $volumeInfo | ForEach-Object { $sizeGB = [math]::Round(($_.Size / 1GB), 2) $sizeRemainingGB = [math]::Round(($_.SizeRemaining / 1GB), 2) $sizeUsedGB = $sizeGB - $sizeRemainingGB Write-Output "DriveLetter: $($_.DriveLetter)" Write-Output "FriendlyName: $($_.FriendlyName)" Write-Output "FileSystemType: $($_.FileSystemType)" Write-Output "DriveType: $($_.DriveType)" Write-Output "HealthStatus: $($_.HealthStatus)" Write-Output "OperationalStatus: $($_.OperationalStatus)" Write-Output "SizeRemaining: $sizeRemainingGB GB" Write-Output "SizeUsed: $sizeUsedGB GB" Write-Output "Size: $sizeGB GB" } |
The above script defines a parameter DriveLetter, allowing administrators to specify a drive letter for which they want to retrieve volume information. By default, it fetches information for the ‘C’ drive.