Category filter
Microsoft Active Directory Integration with Hexnode
Active directory domain services hold all directory information and take care of all the interactions between the user and domain. Any unauthorized user access to a device or a server can be verified using Microsoft Active Directory Integration. With Hexnode, you can manage multiple Active Directory domains from a single console.
Once you integrate Microsoft Active Directory with Hexnode, you will be able to see the users, user groups and subdomains of the linked domain. In order to integrate your Active Directory with Hexnode, you must first configure AD Agent Settings.
Microsoft Active Directory can be integrated with Hexnode by:
- Configuring the Hexnode MDM AD Agent
- Configuring the SSL certificate when LDAPS is enabled in the Active Directory
- Command Line Interface (CLI) method
- Configure the SSL Certificate through Server Manager
- Configuring the Active Directory Settings
- Server Configuration
- Schedule Sync for Microsoft Active Directory
Hexnode MDM AD Agent Settings
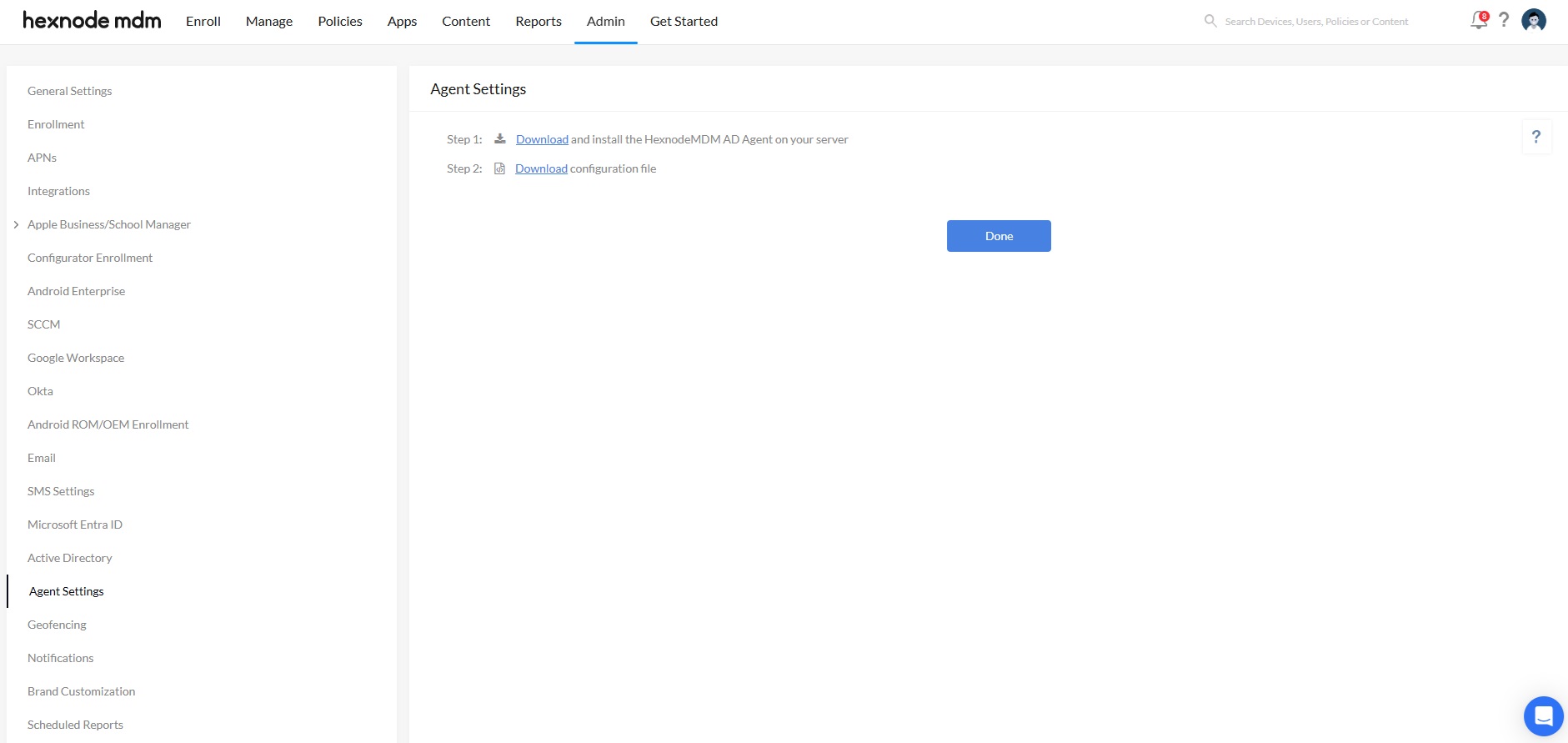
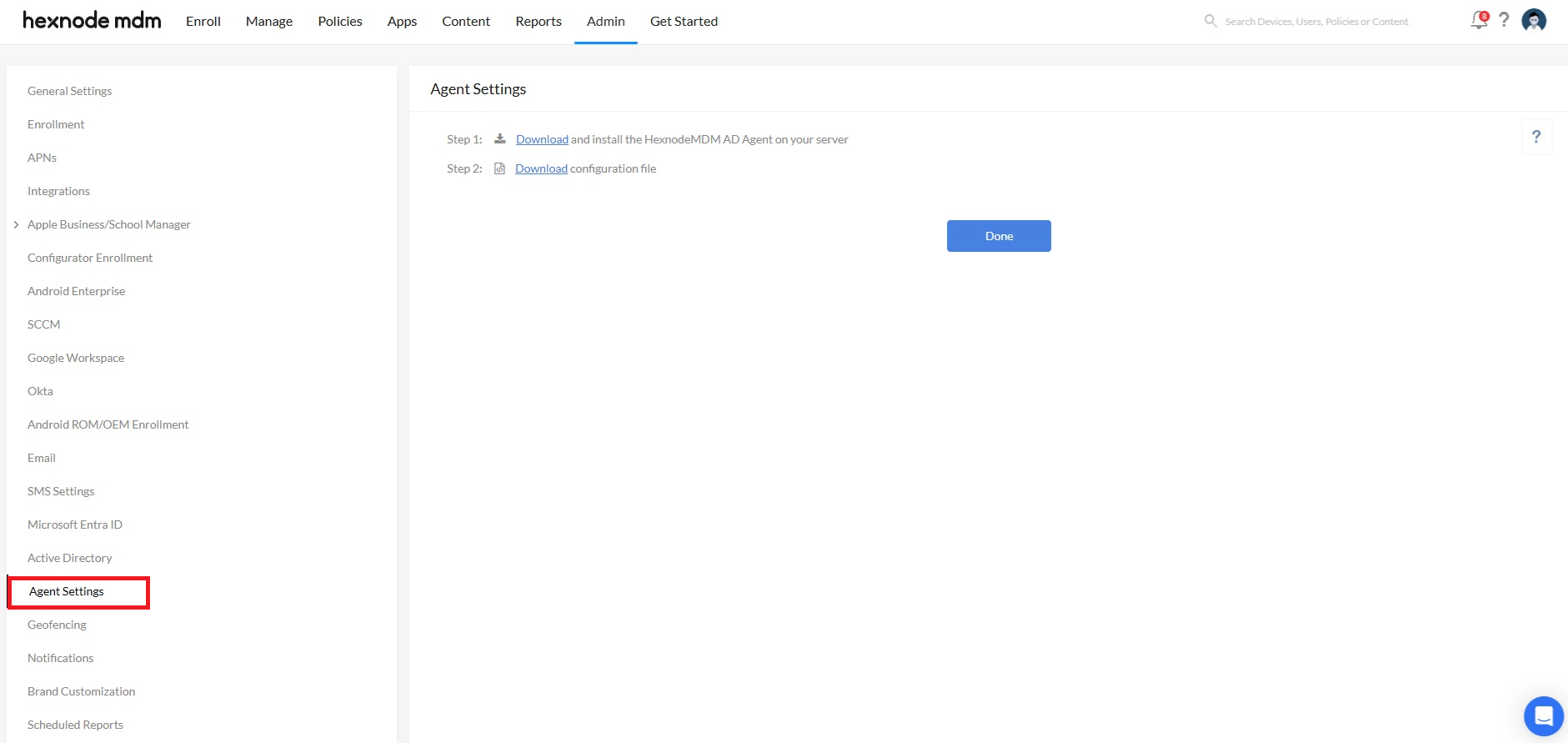
To configure an AD Agent service, click on Admin > Active Directory. This opens up the Agent Settings page when you first configure an Active Directory.
- Click on the Download link to download and install the AD Agent on your server.
- Click on the second Download link to download configuration file.
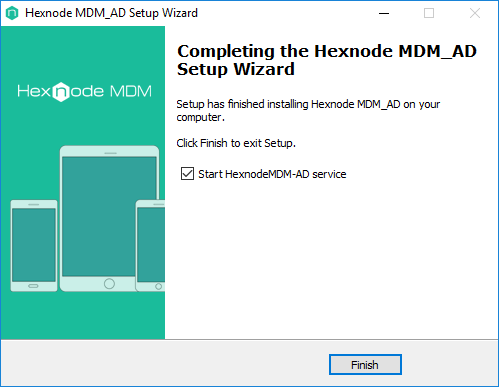
- Launch the Hexnode MDM_AD Setup Wizard. Click on Next to continue or Cancel to exit setup.
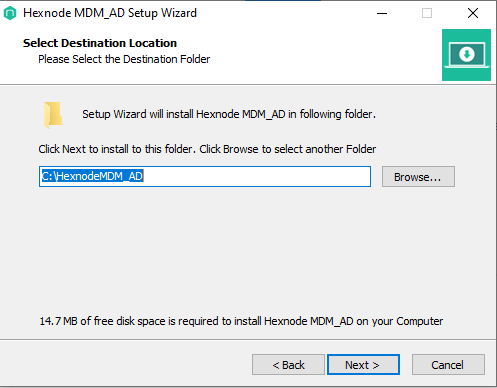
- Select the destination folder where Hexnode MDM_AD will be installed. By default, the setup wizard will install the Hexnode MDM_AD in the folder C:\HexnodeMDM_AD
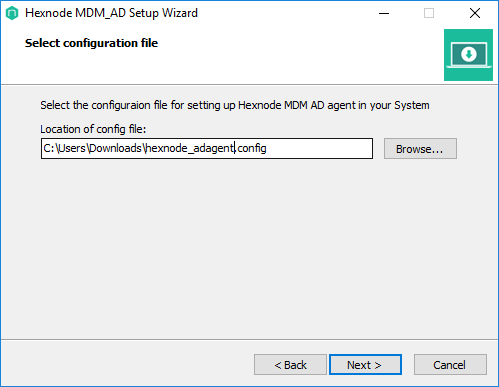
- Select the configuration file downloaded in step 2. Click on Next.
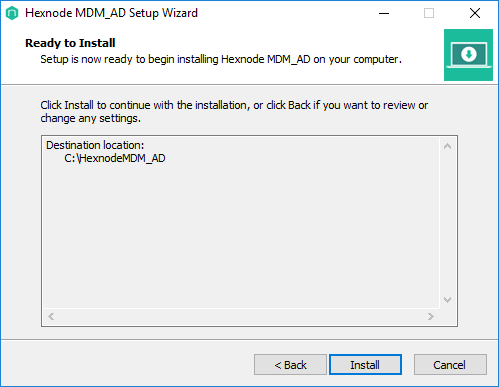
- Once you have uploaded the configuration file successfully, setup will begin installing Hexnode MDM_AD on your computer. Click on Install.
- Click on Finish to exit setup.
- On Hexnode UEM console, click on Done. Now, click on ‘Active Directory‘ to configure Active Directory Settings.
Configuring the SSL certificate when LDAPS is enabled in the Active Directory
LDAPS (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol Safe) is a protocol used to securely connect and access a directory over a network. It ensures a secure connection between the client and the directory server. When LDAPS is enabled in the Active Directory, the admin must upload an SSL certificate to the Hexnode portal. The SSL certificate encrypts the transmitted data and also authenticates the LDAP server. SSL certificates can be obtained by executing a few commands or by configuring the certificates manually through Server Manager. The following are the instructions for each approach.
Command Line Interface (CLI) method
In organizations managing multiple servers, obtaining and configuring the SSL certificates individually is a tedious and inefficient process. Administrators can simplify this by using the following CLI commands to retrieve and encode SSL certificates directly across devices. These commands can be executed on Command Prompt or on the Terminal of the AD Server. The retrieved certificate is stored in the directory where the commands are executed.
|
1 2 |
certutil -ca.cert $CERTIFICATE_NAME.cer certutil -encode $CERTIFICATE_NAME.cer $CERTIFICATE_NAME.cer |
Configure the SSL Certificate through Server Manager
SSL certificates can be manually configured and uploaded to each server. This method can be used in organizations managing a limited number of servers. These SSL certificates can be configured through Server Manager as follows.
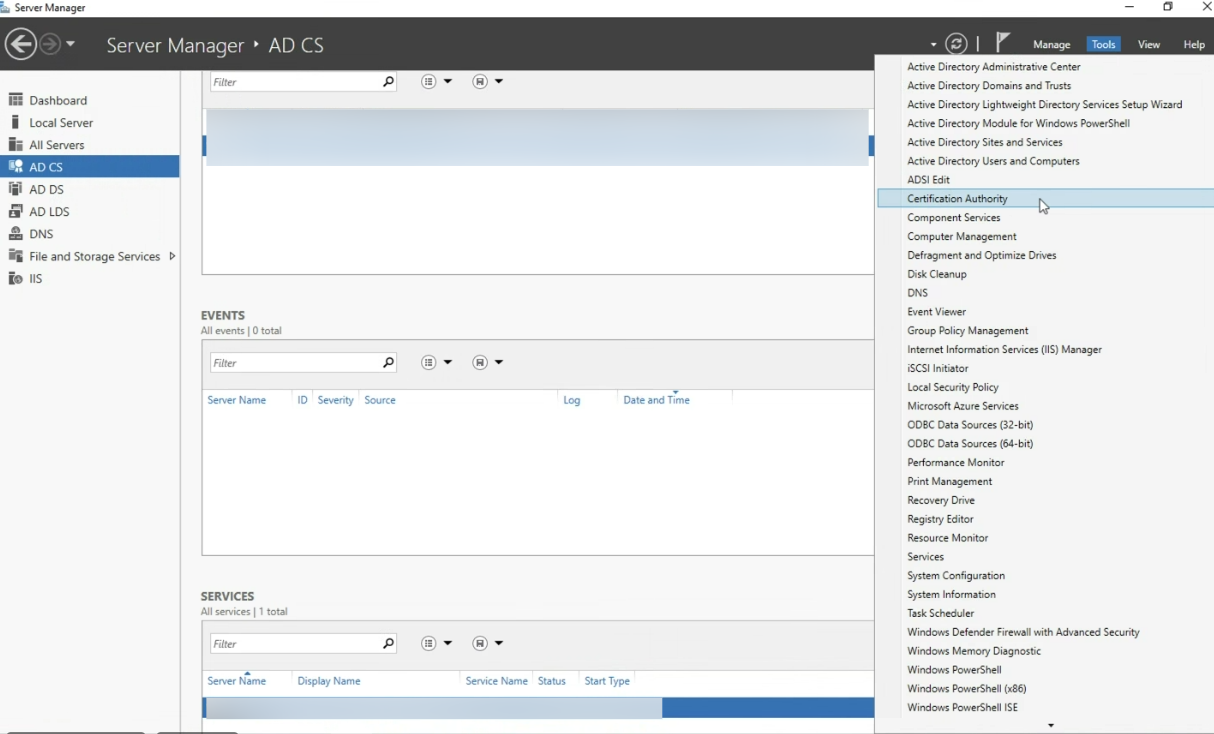
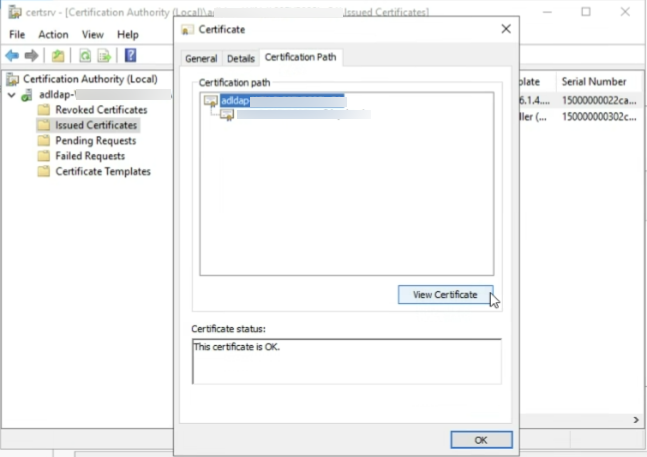
- Access Server Manager > Tools > Certification Authority.
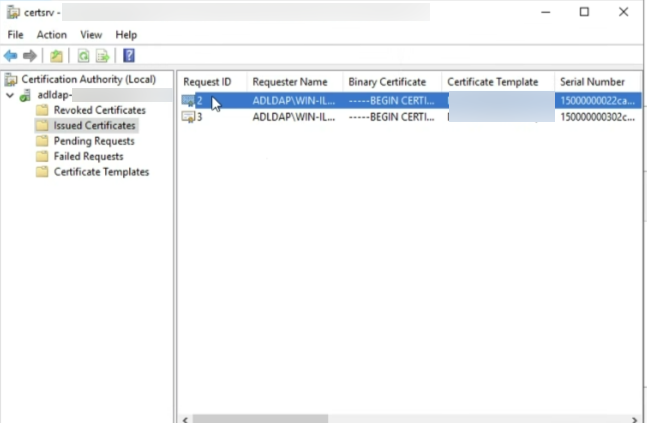
- Navigate to Issued Certificates and click on the certificate listed.
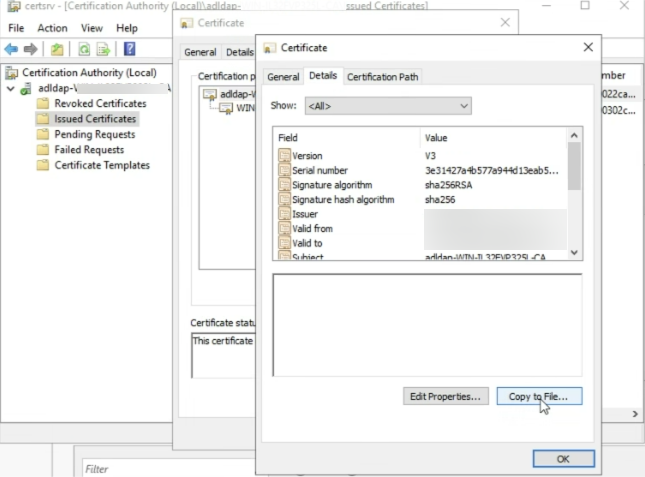
- Navigate to Certification path. Click on the parent certificate and click on View certificate.
- Navigate to Details and click on Copy to File.
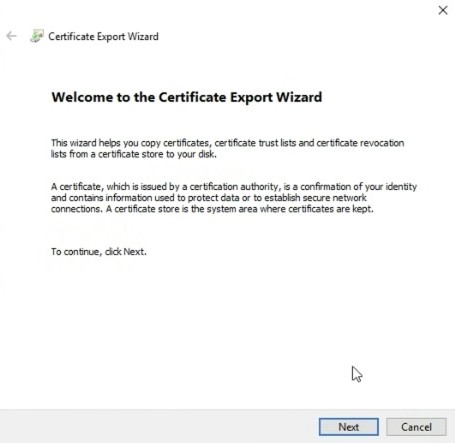
- The Certificate Export Wizard opens and click on Next.
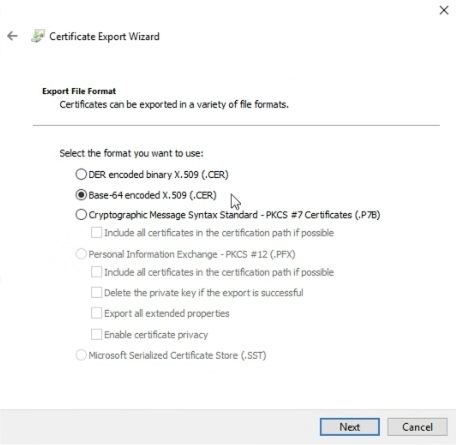
- Select the file format as Base-64 encoded X.509 (.CER). Click on Next.
- Choose the file path. Click on Next. Click on Finish.
- This certificate can be uploaded as the SSL certificate in Server Configuration under Active Directory by browsing it from the selected file path.
Active Directory Settings
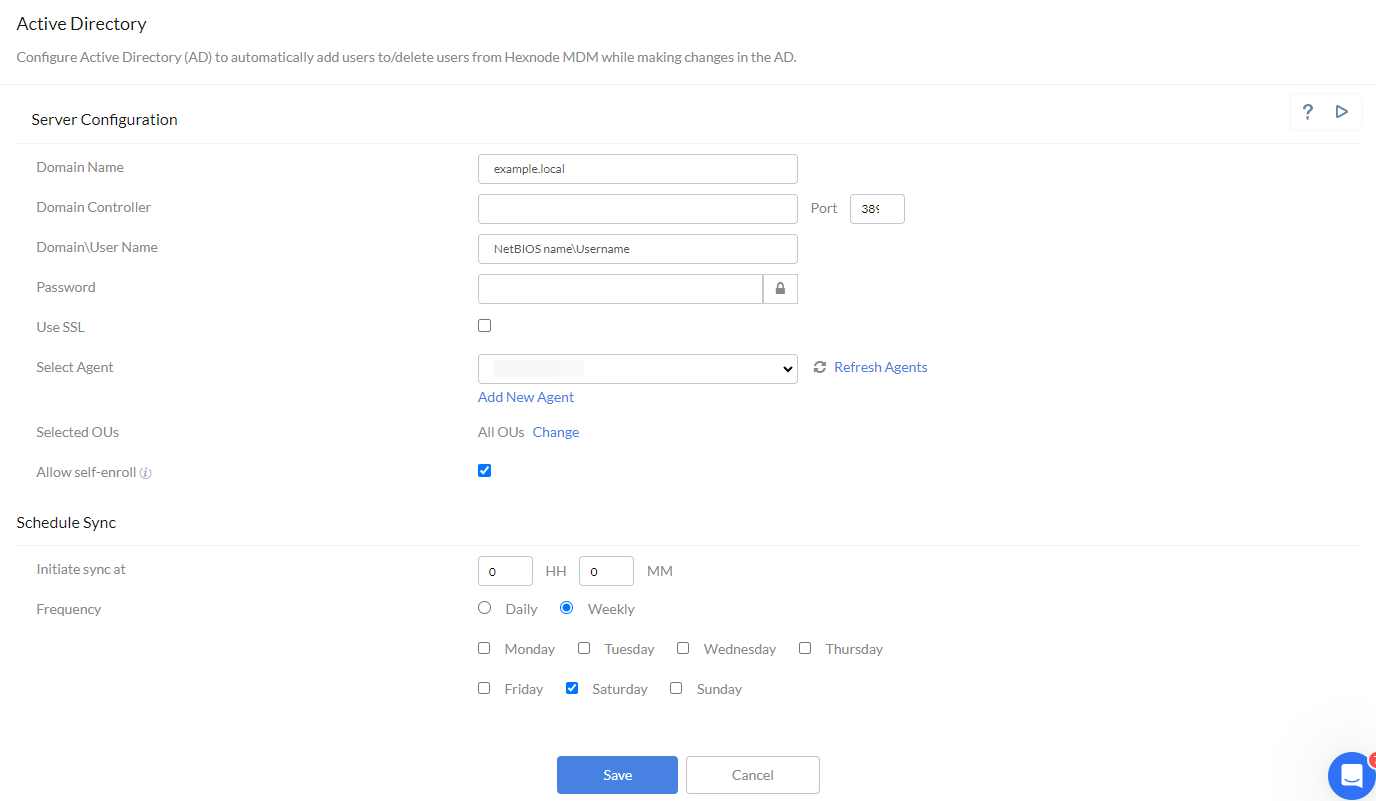
Active Directory Settings include configuring the server and scheduling sync. These settings can be accessed under Admin > Active Directory.
Server Configuration
- Domain Name – Enter the Active Directory Domain Name, which can be the same as the organization’s public domain name, sub-domain or any alternate names that may end in .local.
- Domain Controller – Enter the Domain Controller Name.
- Port – In case LDAPS is enabled, use Port 636. In the case of LDAP, use the default Port 389. Conversely, you can use the port configured by the admin.
- Domain\Username – Enter the Domain Name and Username in the format NetBiosName\SAMAccountName.
- Password – Enter the password.
- Use SSL (when LDAPS is enabled) – Enable the ‘Use SSL’ option and upload the SSL certificate here.
- Select Agent – Select the AD Agent name from the drop-down list. Click on Add New Agent to add a new agent.
- Selected OU’s – By default, all the OUs in the domain will be selected. You can click on Change to select the specific OU’s you want.
- Allow Self Enroll – If you enable the ‘Allow Self Enroll’ option, users in this particular domain will be able to enroll directly from the portal without any enrollment requests.
Schedule Sync for Microsoft Active Directory
You have an option to choose how often you want the AD to be synced with Hexnode UEM. You can schedule daily or weekly sync, select the days of the week and choose the time of the day the sync has to occur.
On clicking Save, your Active Directory will be synced with Hexnode UEM databases.
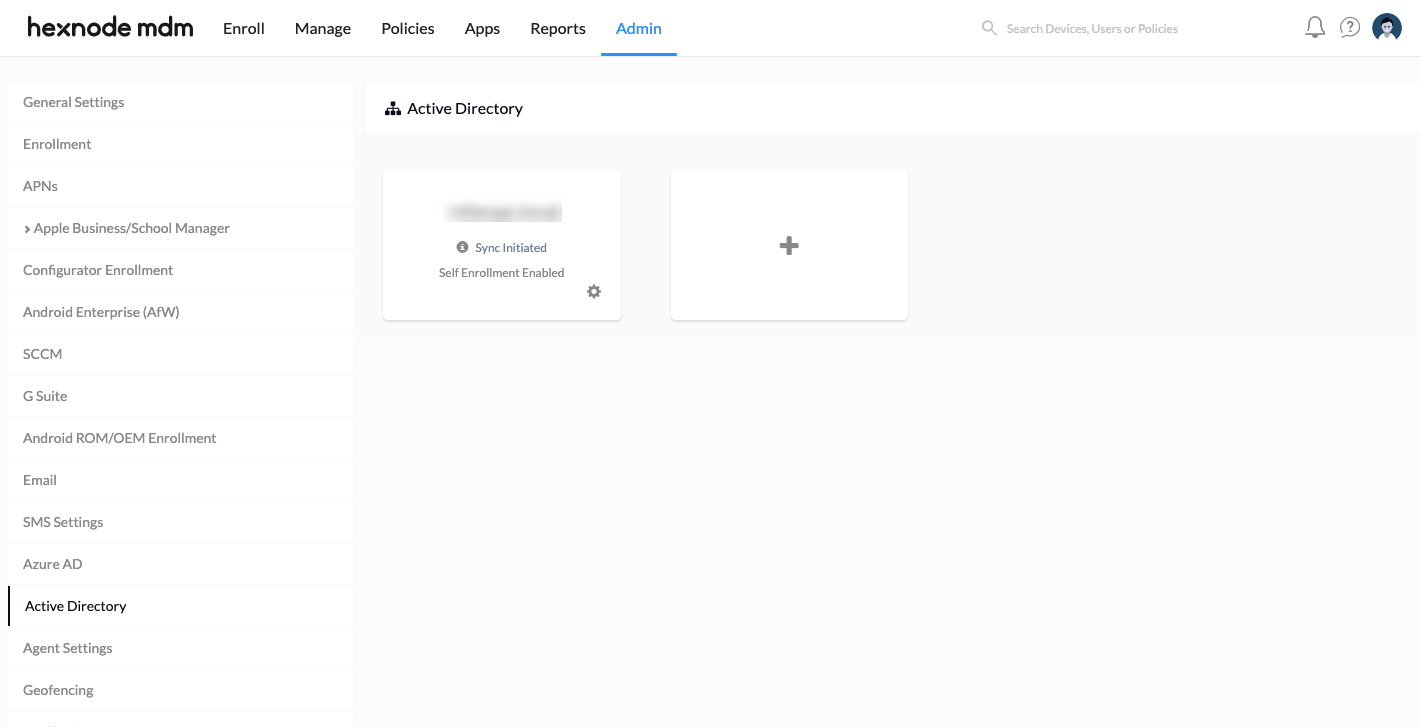
Navigate to Admin > Active Directory.
In the server configuration page, you can add a new agent by clicking on Add new agent.
Similarly, to create a new Active Directory, click on the empty slot with the + sign and configure the settings.
Data fetched from AD
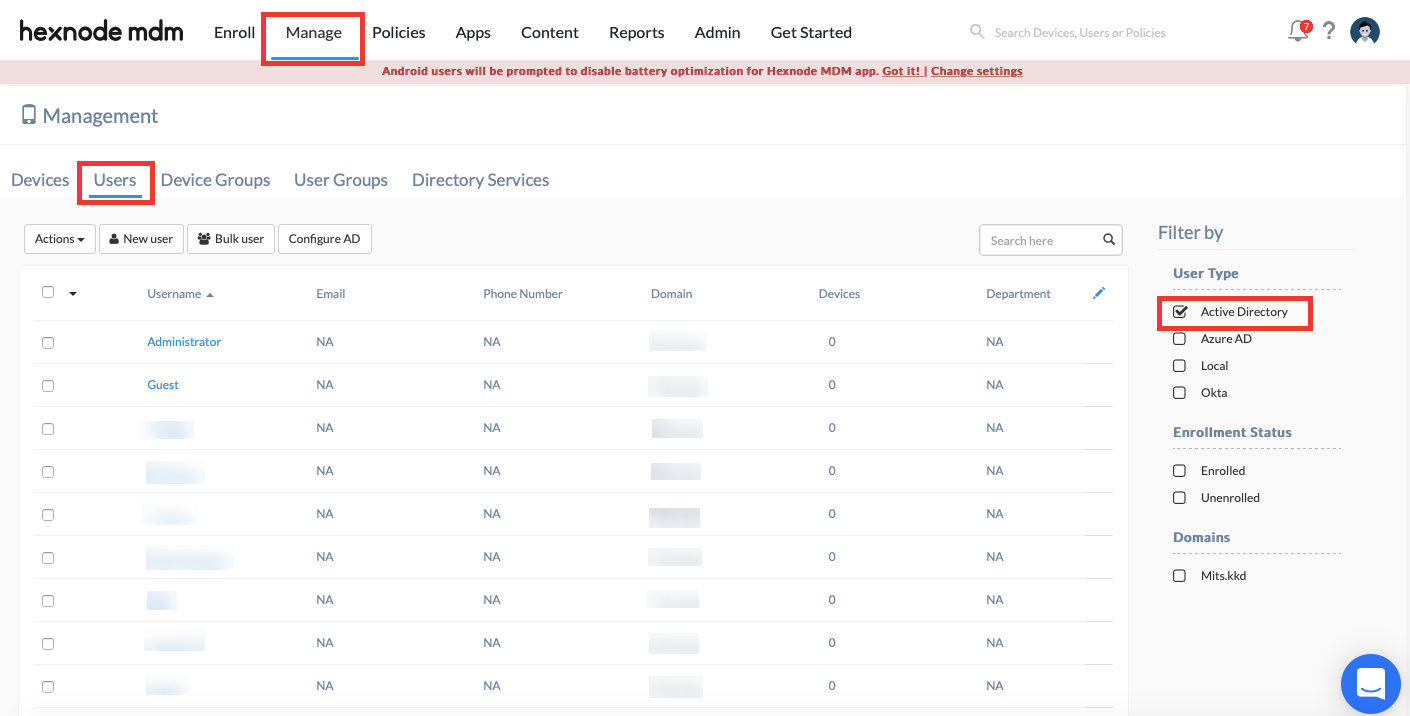
Once the integration is successful, the admin can see the users and user groups under the Manage tab.
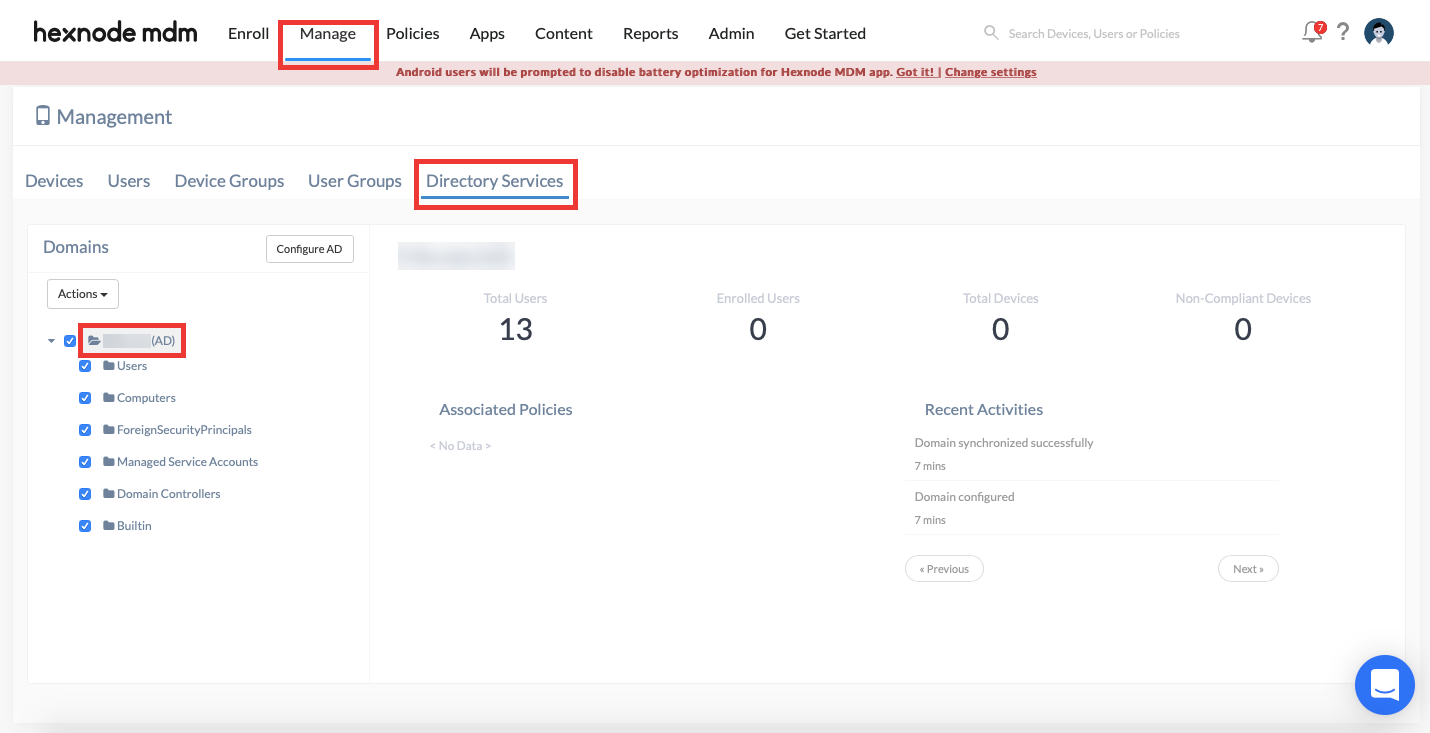
In addition, the Directory Services sub-tab under the Manage tab will have the linked domains listed. This sub-tab displays the recent actions performed on the domain. The admin can also perform actions on the domain here.
Delete AD domain
Hexnode UEM lets users remove their Active Directory domain from the portal with ease.
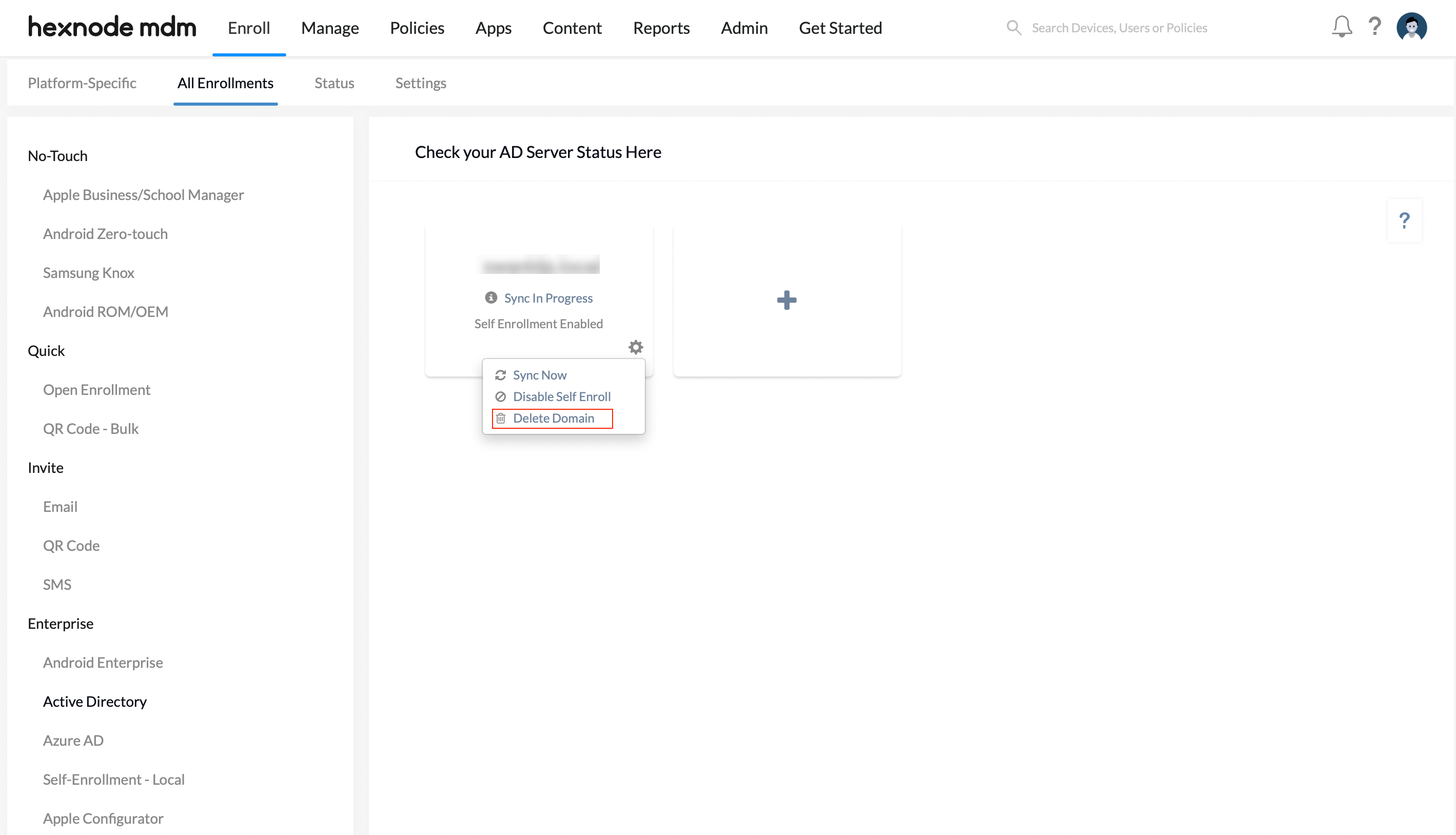
- Access the Delete Domain option by clicking on the settings icon under Enroll > All Enrollments > Enterprise > Active Directory.
- During the deletion process, the administrator is provided with two options.
- Disenroll device(s)
- Assign to a new user
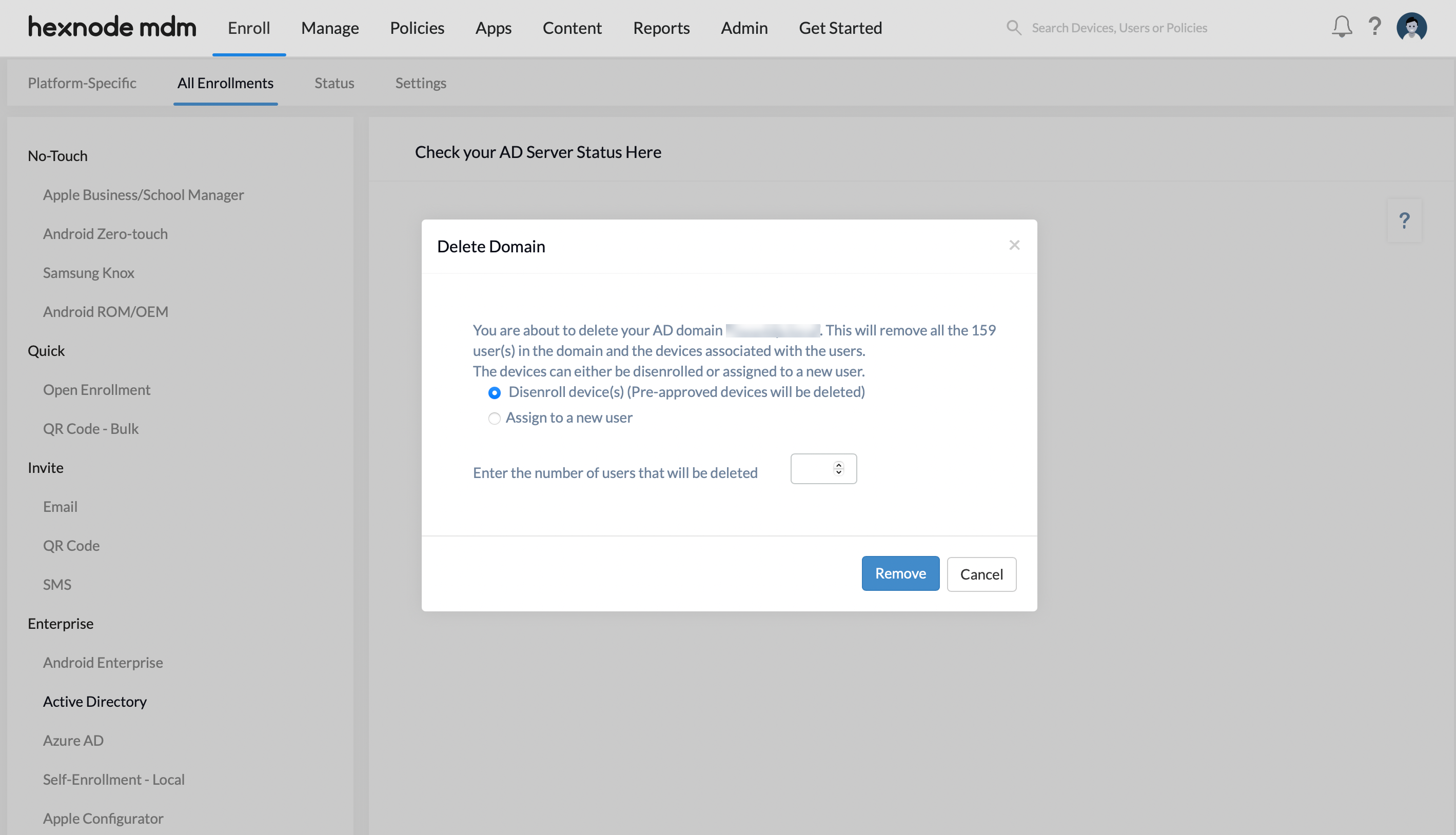
- Disenroll device(s) option removes the Active Directory domain from the portal and disenrolls all devices enrolled under the domain.
- Pre-approved devices will also be deleted from the portal.
- The admin is then required to specify the number of users that will be deleted under the domain and click on the Remove button to complete the process.
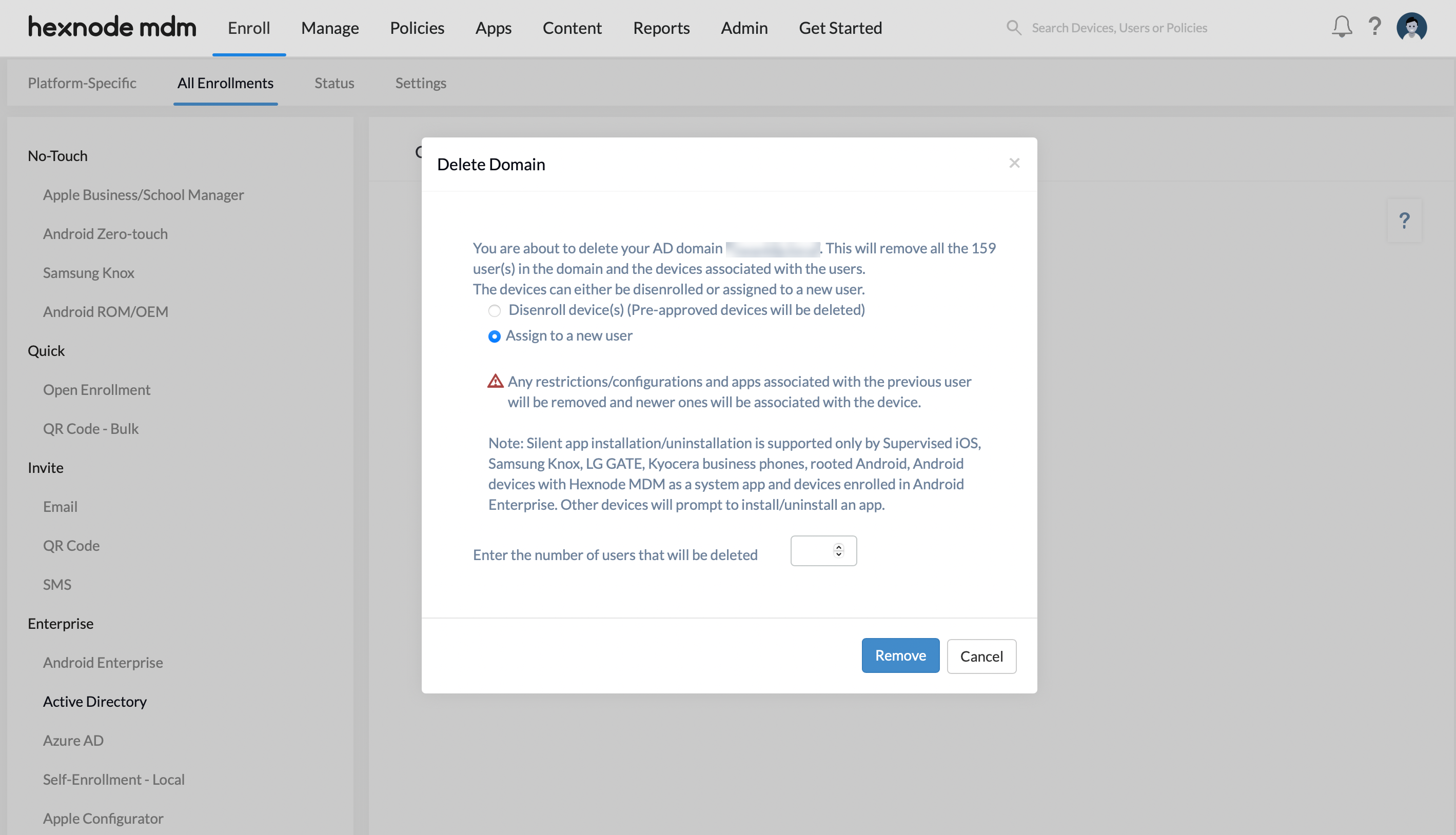
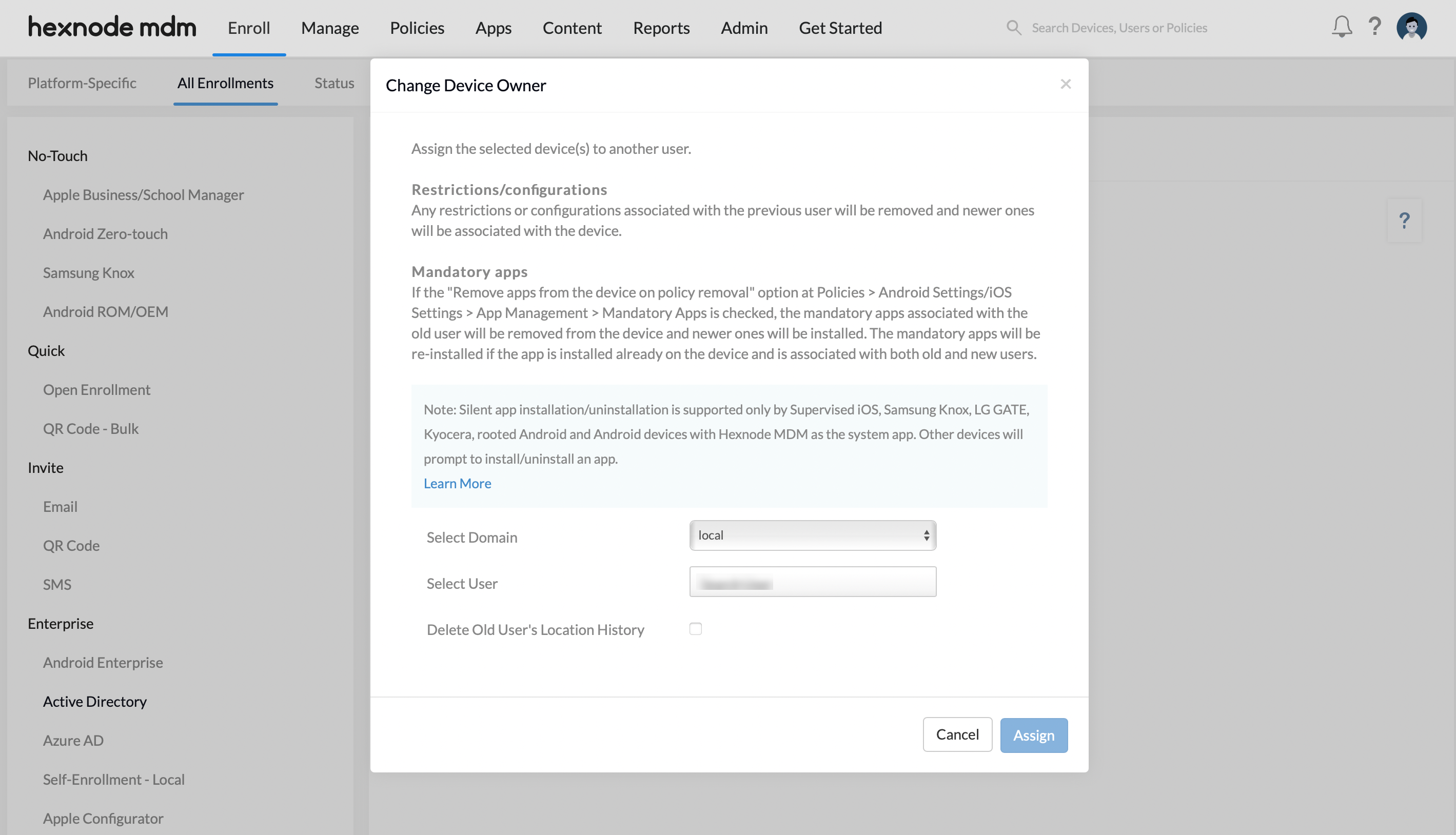
- Assign to a new user option lets the admin assign all devices under the domain to a new user. All existing restrictions/configurations and apps associated with the old user will be removed from the respective device(s).
- After specifying the number of users that will be deleted, click on the Remove button, which will open a dialogue box to assign device(s) to a new user.
- Select the domain and choose the user to assign the devices.
- Toggle the Delete Old User’s Location History checkbox to delete the location history of old users. Click on the Assign button to complete the process.