Category filter
How to set up iOS Global HTTP Proxy settings
Organizations may configure Global HTTP Proxy settings for iOS devices to route the entire HTTP network traffic through the specified proxy server. The proxy server acts as a buffer between the devices and the internet. It has its own IP address on the internet. Thus, it makes sure that any intruders who try to steal confidential data can have access only to the proxy address while maintaining the company’s servers anonymous.
There are times when an organization needs to deploy proxy settings to its multitude of users. Attending to a large number of devices manually can be a daunting task for many administrators. Hexnode simplifies the process of pushing out any proxy settings to iOS devices over the air.
Configure Global HTTP Proxy settings
To set up iOS Global HTTP Proxy settings via policy,
- Log in to your Hexnode MDM portal.
- Navigate to Policies > New Policy. Assign a suitable name and description (optional) for the policy. You can also choose to continue with an existing policy.
- Go to iOS > Security > Global HTTP Proxy. Click Configure.
Global HTTP Proxy Settings
- Proxy type: Select how you are going to set up the proxy. Choose manual or automatic setup and proceed to the section below to know more about the options displayed on the MDM console.
- Allow bypassing proxy to access captive networks: If this option is selected, proxy will be disabled while accessing the login page for captive networks. A captive portal is a web page displayed to the user when he/she tries to access a public-access network. The user needs to interact with this portal and authenticate before access is granted to the network. By default, this option is unchecked.
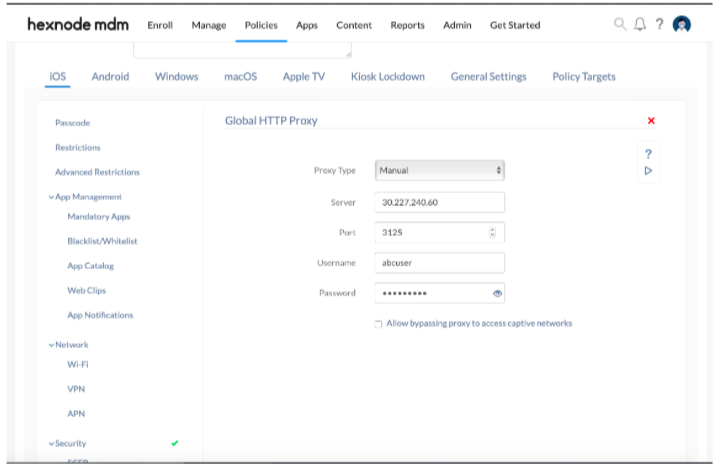
Setting up a manual proxy server
| Manual Proxy Settings | Description |
|---|---|
| Server | Type the IP address or the hostname of the proxy server. This is a mandatory field. |
| Port | Enter the port number of the proxy server used for connecting to the client. The default value is 8080. This is a mandatory field. |
| Username | Private proxies require a username to use its services. |
| Password | Give the password associated with the username of the private proxy server. |
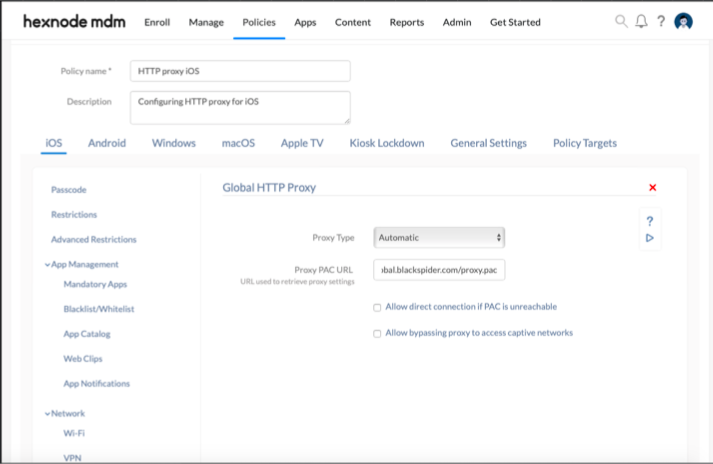
Setting up automatic proxy server
| Automatic Proxy Settings | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| Proxy PAC URL | PAC files are used to configure the proxy settings. They have JavaScript functions that configure necessary settings.
Eg: Provide the URL to the configuration script. Whenever a new URL is loaded, the given PAC URL is referenced. The URL is evaluated based on the functions in the PAC file. The functions decide if the proxy should be used or not. This is a mandatory field. |
|
| Allow direct connection if PAC is unreachable | If disallowed, the device is restricted from connecting to the destination address when the PAC file is unreachable. | Disallowed |
Associating the policy with devices/groups
Method 1: If the policy has not been saved,
- Navigate to Policy Targets > +Add Devices.
- Choose the target devices and click OK. Click Save.
- You can also associate the policy with device groups, users, user groups or domains from the left pane of the Policy Targets tab.
Method 2: If the policy has been saved,
- Go to Policies and choose the desired policy.
- Click on the Manage drop-down and select Associate Targets.
- Choose the target entities and click Associate.
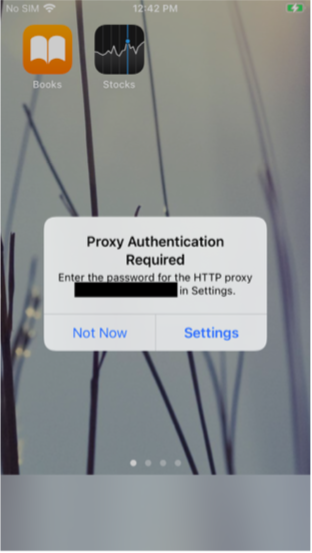
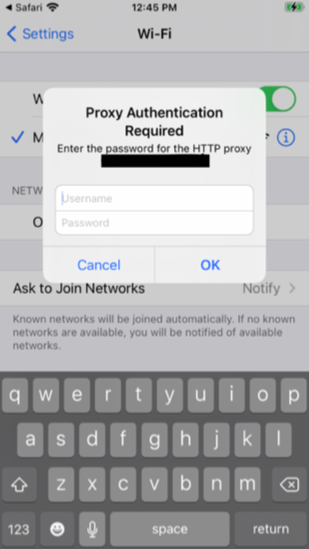
What Happens at the Device End?
After the successful association of the policy, a prompt appears on the device. The prompt provides the user with two options- “Not Now” and “Settings” . Selecting “Not Now” will make the prompt disappear momentarily, and the user can continue with his tasks but will not be able to access the internet. On choosing “Settings”, the user is directed to the Settings app of the device. Here, another prompt appears, asking to either sign in by entering the username and password or to cancel the prompt. The prompt can be canceled but keeps reappearing till the user signs in. During this time, access to the internet will be restricted even if the device is connected to the Web. The user needs to sign in to the proxy to regain access to the internet.