Category filter
Enroll Windows Virtual Machines in Hexnode UEM
Developing, supporting, and monitoring a massive test environment is tedious and time-consuming. To ease such a burden, virtualization allows you to deploy multiple virtual machines (VMs) on a single system. You can install another OS using a virtual machine and then control it on your Windows desktop at your convenience without rebooting or having several hard drives or distinct partitions.
What is a Virtual Machine?
A virtual machine act as a separate computer within your computer. Users will experience no difference from a separate computer since it is run in a different window on the host computer. However, since virtual machines are sandboxed from the host computer, it remains unaffected by the operations of the host.
This guide will be based on setting up a virtual machine using VirtualBox since it is one of the most popular VM programs. However, keep in mind that several VM programs are available and most VM apps similarly handle creating a virtual machine.
How to set up a Virtual Machine (VirtualBox)?
Download the Disc Image (ISO file)
Ensure you have sufficient free hard disc space to install your preferred operating system. Next, you’ll require that OS, typically as an ISO file. For installing Windows 10/11, the media creation tool is required to create an ISO file.
- Download and run the media creation tool for Windows 10 or Windows 11.
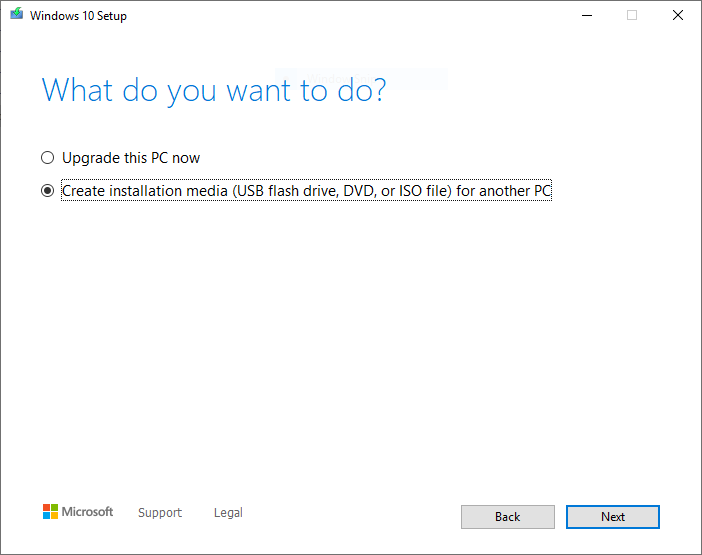
- Choose Create installation media (USB flash drive, DVD, or ISO file) for another PC. Click on Next.
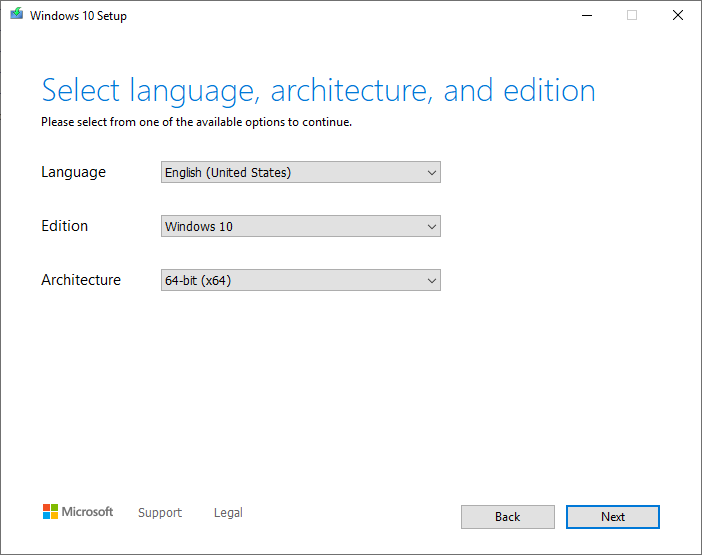
- Pick the preferred language, edition and architecture of Windows. Click on Next.
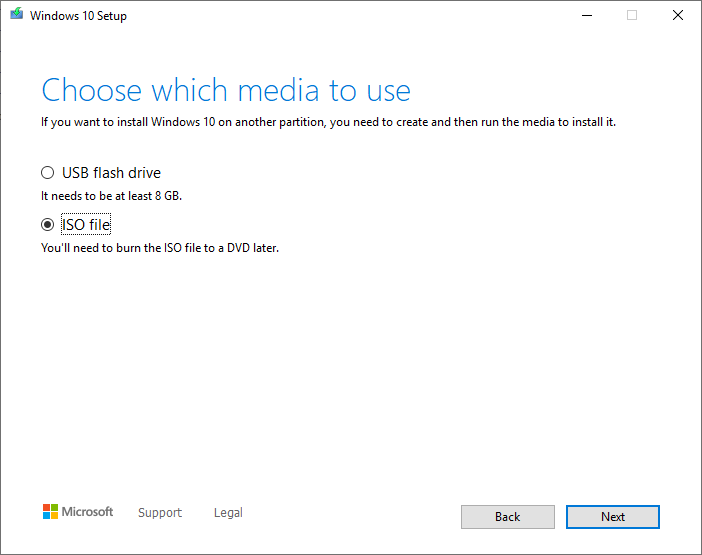
- Choose an ISO file as the media to use for installation. Click on Next.
- Finally, the ISO file will be created.
Install and Create VirtualBox (Virtual machine by Oracle)
- Download the latest version of Oracle’s free and open-source software, VirtualBox.
- Complete the installation and launch Oracle VM VirtualBox Manager.
- Click on the New icon at the top of the window to create a virtual machine (VM).
- Provide a Name for the VM and choose the Machine Folder, Type and Version of OS you expect to be installed. Click on Next.
- Allocate the accessible memory size for the VM. Here, you can use the default RAM or change it as convenient. Click on Next.
- Next, create a virtual hard disk by selecting Create a virtual hard disk now. Click on Create.
- Choose the hard disk file type as VDI (VirtualBox Disk Image). Click on Next.
- From the given options, you can select if the hard disk file size should be Dynamically allocated or be a Fixed size. Click on Next.
- Finally, provide a name and confirm the size of the created virtual hard disk file. Click on Create.
![]()






Install Operating System on Virtual Machine
Once the virtual machine creation is completed,
- Start the created VM by clicking on Start.
- From the ‘Select start-up disk’ window, choose the Windows 10/11 ISO file downloaded earlier.
- Finally, click on Start to install the OS on your VM.

Launch the Windows Installer
Once the setup is completed, click on the Start button in VirtualBox and follow the on-screen instructions for the Windows 10/11 installation process.

Manage Virtual Machine using Hexnode UEM
Virtual machines can be set up on personal computers and enrolled using Hexnode UEM for remote management. This can be used as a workaround for Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) devices. To manage a virtual machine using Hexnode UEM, enroll the VM in the UEM portal to establish a connection between the UEM and VM. Refer to our detailed guide on enrolling Windows PCs for a detailed step-by-step walkthrough.

