Category filter
Deploying ThreatLocker to Windows devices with Hexnode UEM
ThreatLocker, a zero-trust endpoint protection platform, provides robust cybersecurity solutions to organizations, ensuring continuous verification and protection against potential threats. ThreatLocker protects endpoints from a wide variety of threats, including phishing, malware, ransomware, rootkits, password attacks, and IoT attacks. This document will assist you through the step-by-step process to deploy ThreatLocker to Windows devices with the help of Hexnode UEM guaranteeing strong protection against cybersecurity threats.
How to deploy ThreatLocker to Windows?
Follow these steps to deploy ThreatLocker to Windows endpoints:
- Download the PowerShell script from the ThreatLocker portal to deploy ThreatLocker on the devices.
- Login to your ThreatLocker portal.
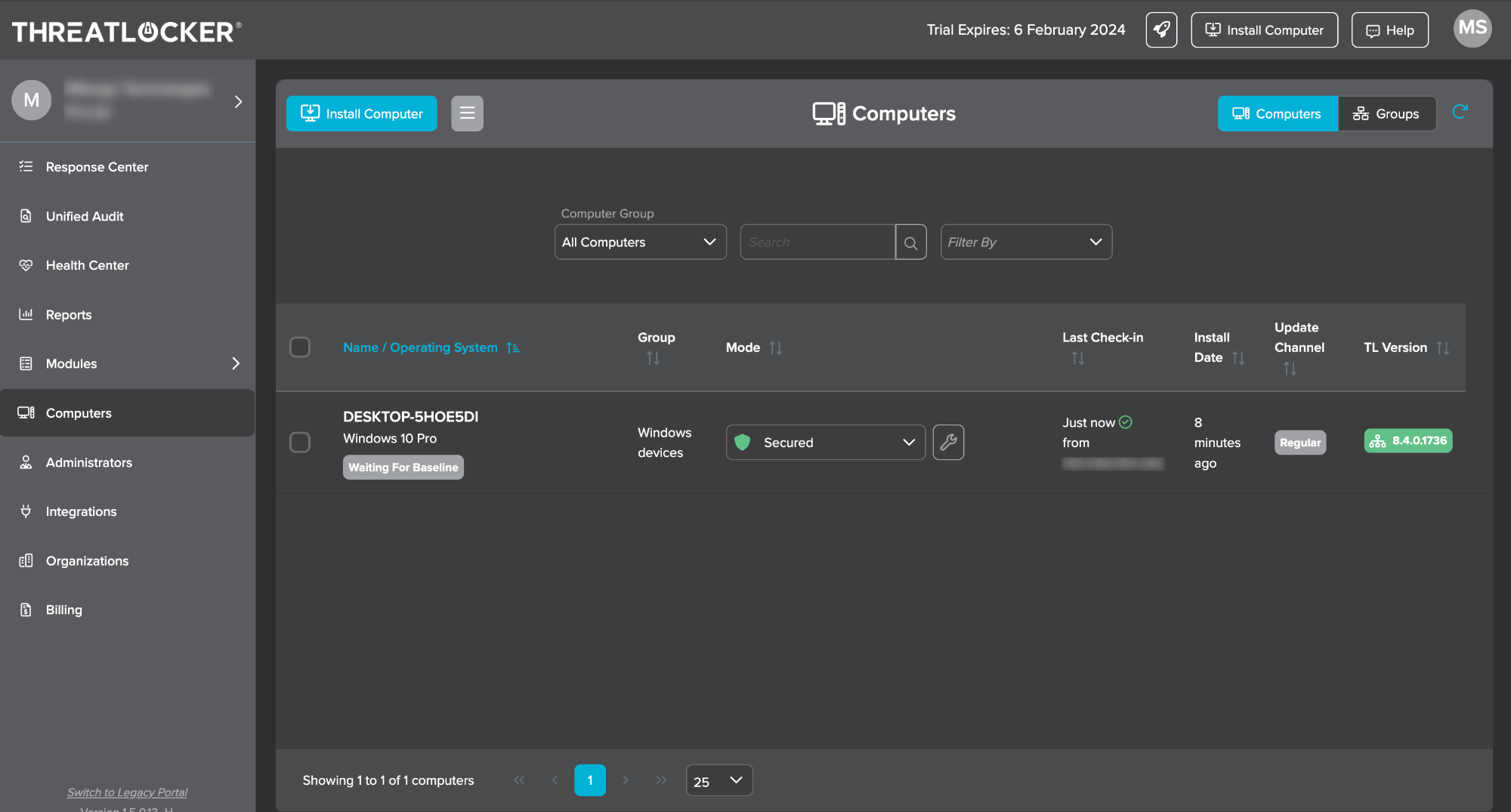
- Click the option Computers from the navigation panel.
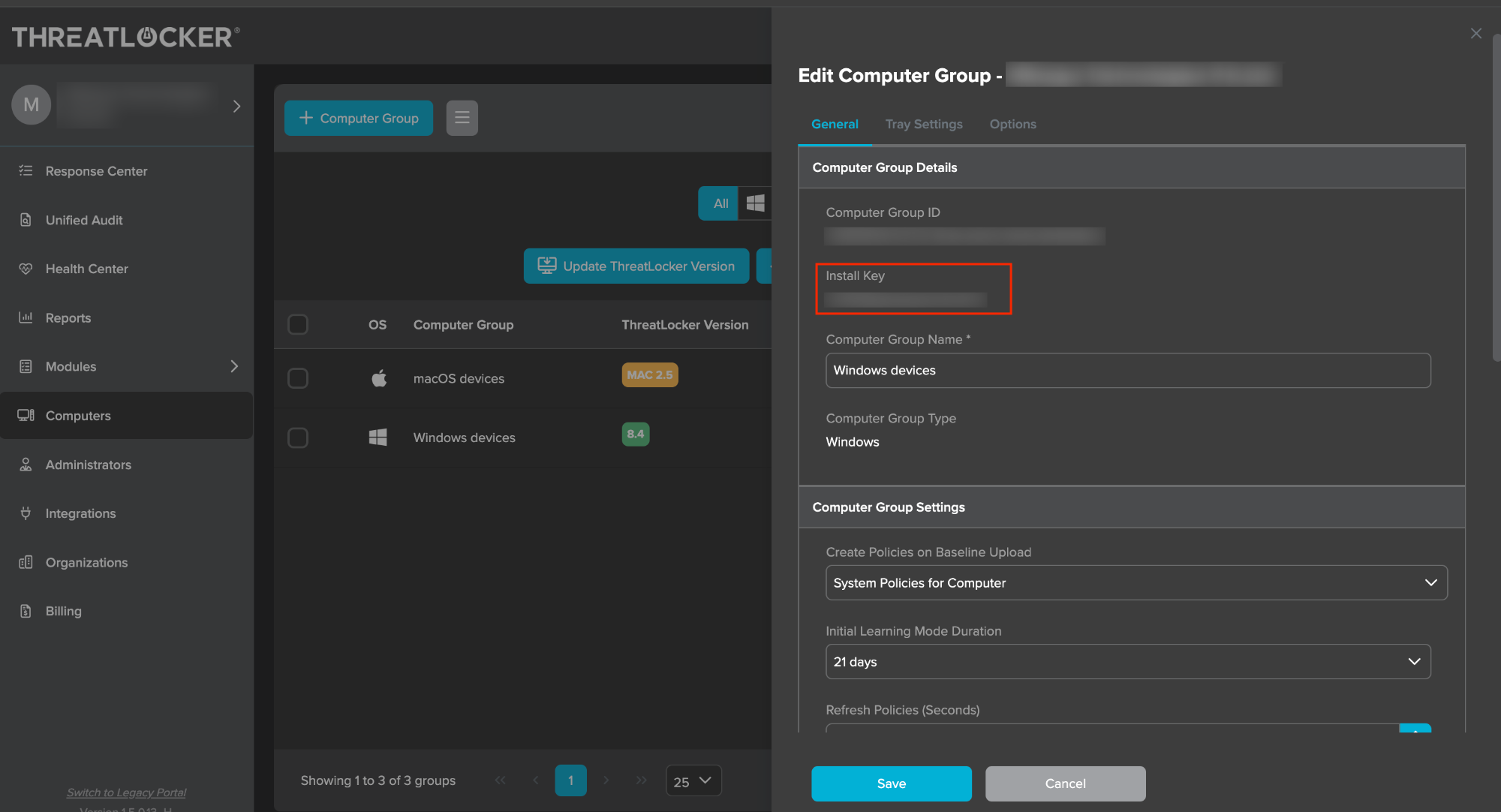
Create a new group for the Windows devices by navigating to option +Computer Group and providing the details of the group. - After creating the group, the Install Key value can be obtained from the device group information in the ThreatLocker portal. This will be used to replace the
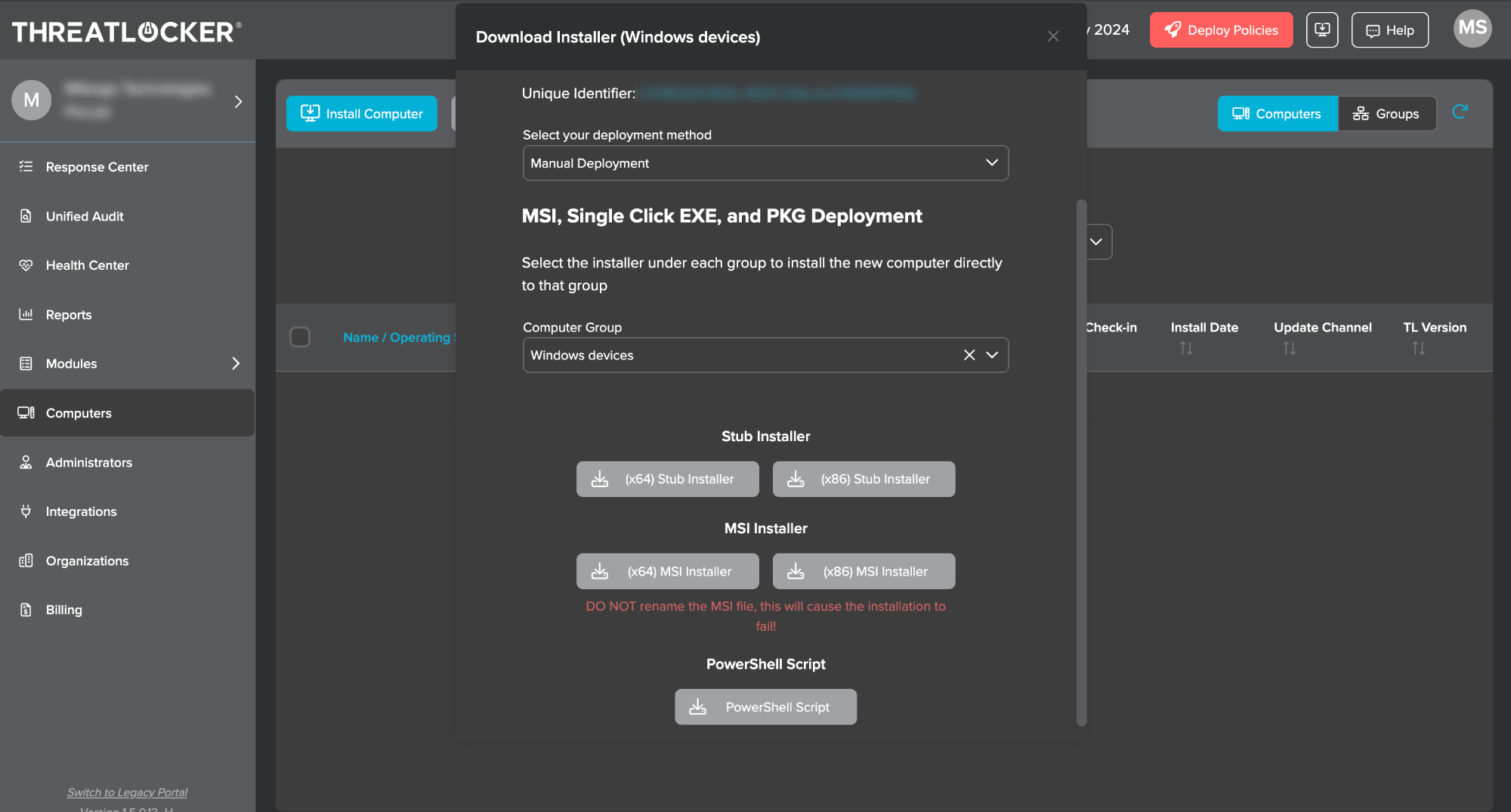
Groupkeyin the PowerShell script. - Click the option Install Computer and select deployment method as Manual Deployment and Computer Group as the group created for the Windows devices.
- Then an option to download the PowerShell script will appear in the same tab.
- Download the PowerShell script.
- Execute the script to deploy ThreatLocker to the devices.
- Login to Hexnode UEM portal.
- Go to the Manage tab and select the device.
- Click on the Actions drop-down and select the Execute Custom Script option.
- Click Choose file to upload the PowerShell script downloaded from the ThreatLocker portal. The script is given below:
ThreatLocker installation script
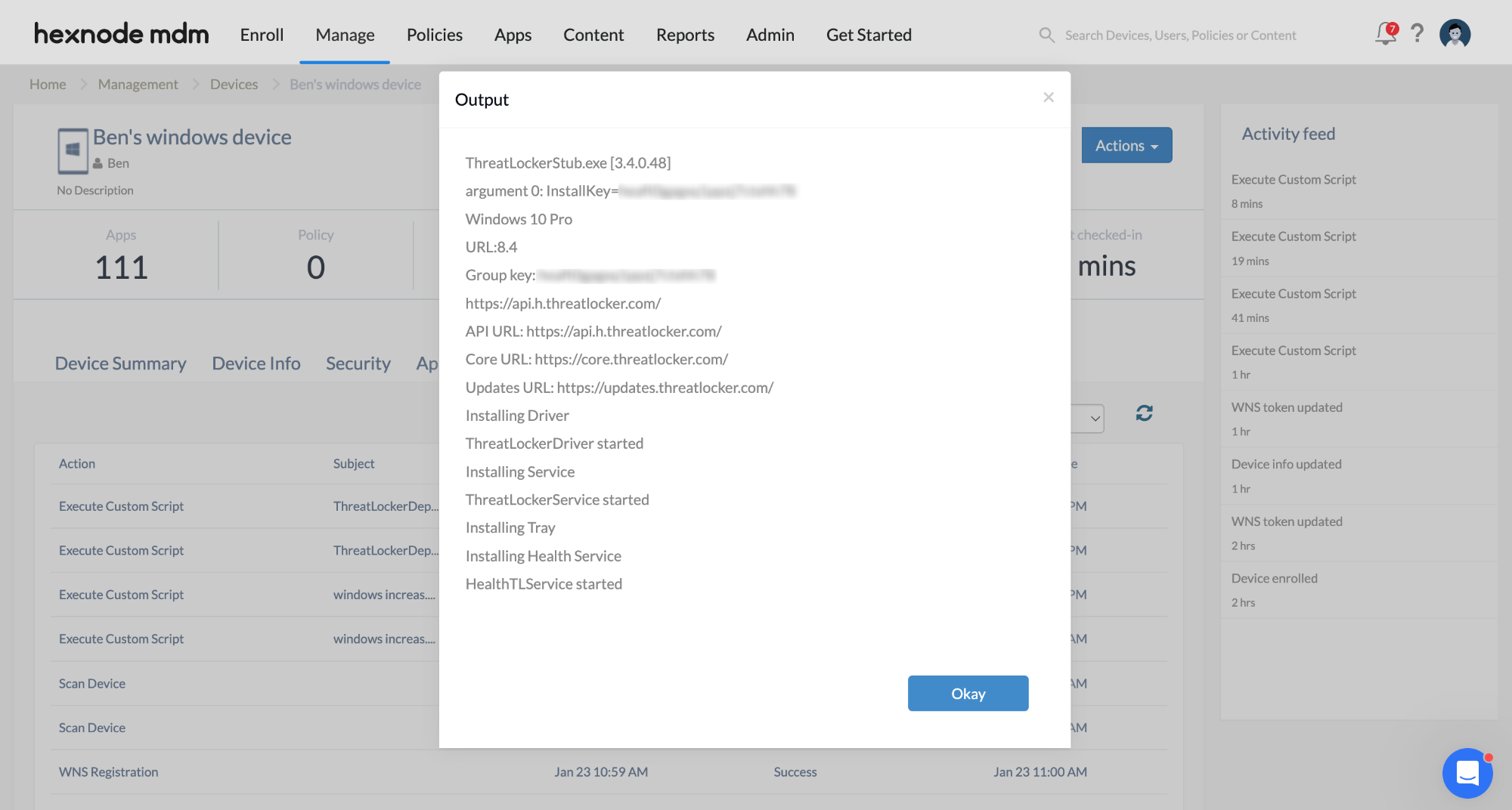
1234567891011121314151617181920212223242526272829303132333435363738#!/bin/bashGroupKey="xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx"# Check for ThreatLocker appif [ ! -d /Applications/Threatlocker.app ]; then# Make API call and extract version numberVersion=$(curl -H "InstallKey: $GroupKey" https://api.threatlocker.com/getgroupkey.ashx | awk -F ':' '/URL/ {print $2}')# Check if Version is retrievedif [ -z "$Version" ]; thenecho "Unable to retrieve version number"exit 1fi# Download the specific version of ThreatLockercurl --output "/private/var/tmp/Threatlocker.app.zip" "https://updates.threatlocker.com/repository/mac/$Version/Threatlocker.app.zip"# Unzip and installunzip -qq /private/var/tmp/Threatlocker.app.zip -d /Applicationsif [ ! -d /Applications/Threatlocker.app ]; thenecho "Not able to download the file"exit 1elseopen /Applications/ThreatLocker.app --args -groupKey $GroupKeyecho "Installing Threatlocker"sleep 15echo "Verifying Group Key"sleep 15if [ ! -d /Library/Application\ Support/Threatlocker ]; thenecho "GroupKey is Invalid"exit 1elseecho "Threatlocker Installed"exit 0fififi# Check if ThreatLocker is already installedif [ -d /Applications/ThreatLocker.app ]; thenecho "Threatlocker is already installed"exit 1fi - Click Execute.
- Navigate to the Action History tab of the device to check if the ThreatLocker has been installed successfully.
- In the ThreatLocker portal, navigate to the Computers section to view the devices on which the ThreatLocker is deployed.
What happens at the device end?
Once the deployment is successfully completed, the devices will be added to the ThreatLocker portal. It helps ensure that the devices are actively protected against a wide range of threats, including phishing, malware, ransomware, rootkits, password attacks, and IoT-related vulnerabilities.