Category filter
How to configure VPN on macOS devices?
A Virtual Private Network allows users to remotely connect to the organizational network, ensuring secure access to corporate resources. Moreover, the VPN can also be configured to route all the traffic through the specified network. The IT admin can configure a VPN server settings on macOS devices via a policy in Hexnode UEM, which, when associated with target entities, sets up VPN configurations in the devices and creates new connections to the network.
Configure VPN server settings via policy
To configure VPN settings for your macOS devices securely using a policy,
- Login to your Hexnode UEM portal.
- Navigate to Policies > New Policy. Assign a suitable name and description (optional) for the policy. You can also choose to continue with an existing policy.
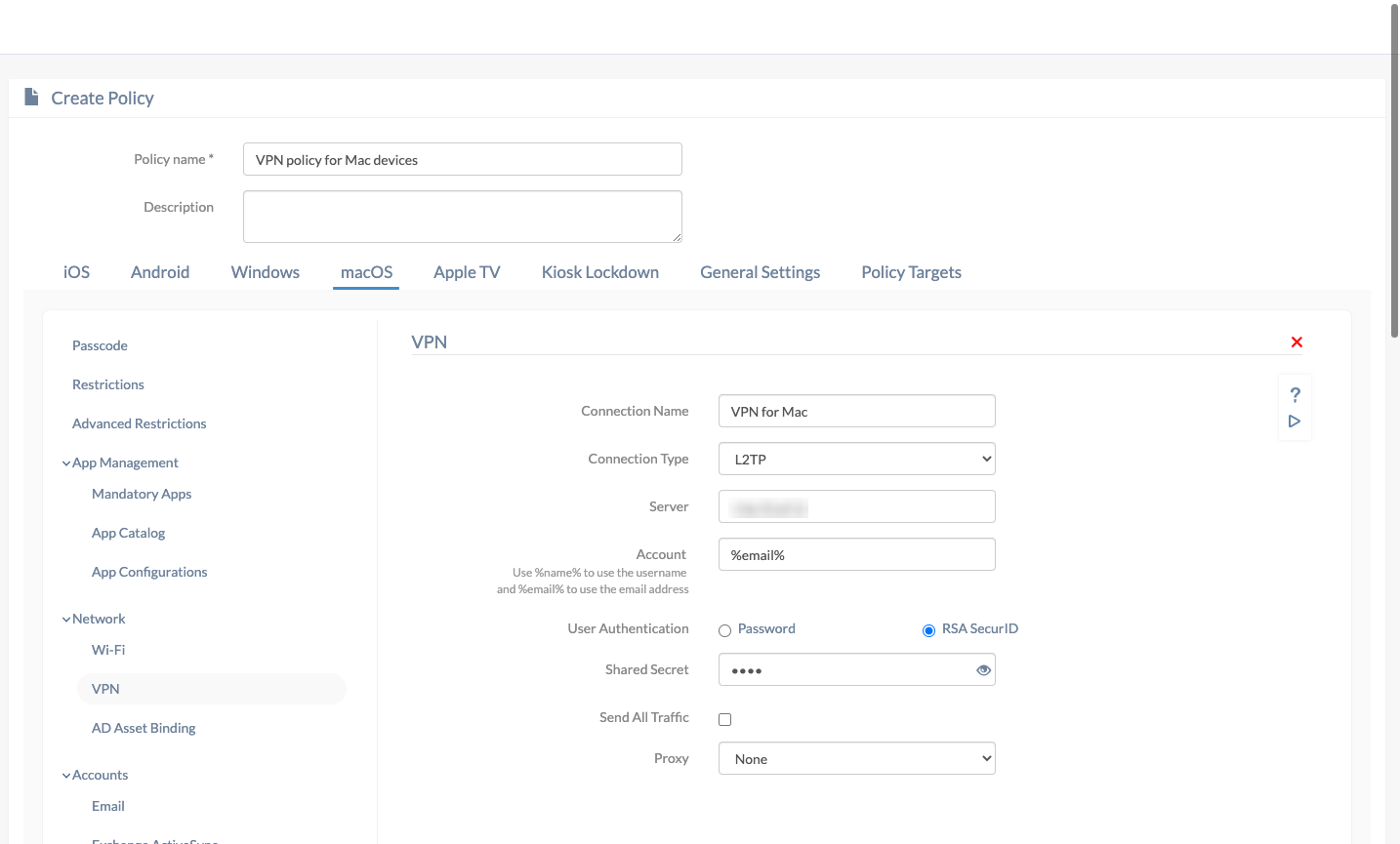
- Go to macOS > Network > VPN. Click Configure.
| Settings | Description |
|---|---|
| Connection name | A name for the VPN configuration for identification in case multiple VPNs are configured. If the policy is associated with a target, the configured connection name will be displayed among the list of available VPN connections on the device. |
| Connection type | Choose a connection type from the list. Further options will change according to the connection type you’ve chosen. L2TP (default), PPTP, IPSec (Cisco), Cisco AnyConnect, Juniper SSL, F5 SSL, SonicWALL Mobile Connect, Aruba VIA, Check Point Mobile VPN and Open VPN are the available options. |
| Server | Enter the IP address or Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) of the VPN server. |
| Account | The username of the user required to get connected with the VPN server. This field supports the use of wildcards. The supported wildcards are
|
Configuring L2TP
| Settings | Description |
|---|---|
| User authentication | The method with which a device can be authenticated with the VPN server. The two available options are “Password” and “RSA SecurID” (default). |
| Password
(If user authentication is selected Password) |
Password required to connect to the VPN. |
| Shared secret | A second password required to establish a connection. Also known as pre-shared key, the shared secret is previously known to the device and the VPN server, and no one else. This key is used just to establish a connection and not used for encryption. |
| Send all traffic | All network traffic will be sent through the VPN, disabled by default. |
Configuring PPTP
| Settings | Description |
|---|---|
| User authentication | Select how the device needs to be authenticated with the VPN server. The available options are “Password” and “RSA SecurID” (default). |
| Password
(If user authentication is selected Password) |
The password to connect to the VPN server. |
| Encryption level | Describe how secure the encryption should be. The available values are None (default), Automatic, Automatic (128 bit). |
| Send all traffic | Send all network traffic through the VPN, disabled by default. |
Configuring IPSec (Cisco)
| Settings | Description |
|---|---|
| Password | The password required to connect to the VPN server. |
| Machine Authentication | Two options are available: Certificate and Group Name/ Shared Secret (default). |
| Certificate
(If machine authentication is selected Certificate) |
Select a certificate from the list. If no certificates are listed, upload the same at macOS > Security > Certificates and they’ll be listed here. |
| Include user PIN
(If machine authentication is selected Certificate) |
Prompts the user to enter the PIN while the connection is made, disabled by default. |
| Group name
(If machine authentication is selected Shared secret/Group name) |
The group name of the connection. |
| Shared secret | A key known to the VPN server and the device which is used to establish a connection between the two. |
| Use hybrid authentication | Use the group name, shared secret and a server-side certificate for authentication. disabled by default. |
| Prompt for password | The device asks the user to provide a password to get authenticated to the VPN server, disabled by default. |
Configuring Cisco AnyConnect
| Settings | Description |
|---|---|
| Group | The group name of Cisco AnyConnect VPN. |
| User authentication | Select how the device needs to be authenticated with the VPN server. The available options are “Password” (default) and “Certificate”. |
| Password
(If user authentication is selected Password) |
The password to authenticate to the VPN server. |
| Certificate
(If user authentication is selected Certificate) |
Select the required certificate from the list if it is uploaded at macOS > Security > Certificates. |
Configuring Juniper SSL
| Settings | Description |
|---|---|
| Realm | The realm is the server to which the device needs to be connected. |
| Role | Specify here the resources which the user can access. |
| User authentication | Select how to authenticate with the VPN. The available options are “Password” (default) and “Certificate”. |
| Password
(If user authentication is selected Password) |
The password for authenticating with the VPN server. |
| Certificate
(If user authentication is selected Certificate) |
Select a certificate from the list. To have a certificate displayed here, upload it at macOS > Security > Certificates. |
Configuring SonicWALL Mobile Connect
| Settings | Description |
|---|---|
| Login group or domain | The name of the login group or domain. |
| User authentication | Choose how to authenticate with the VPN. The available values are “Password” (default) and “Certificate”. |
| Password
(If user authentication is selected Password) |
Provide the password associated with the VPN username. |
| Certificate
(If user authentication is selected Certificate) |
Choose a certificate from the list. If no certificates are listed, upload them at macOS > Security > Certificates. |
Configuring F5 SSL, Aruba VIA, Check Point Mobile VPN and Open VPN
| Settings | Description |
|---|---|
| User authentication | Select the method for authenticating with the VPN server. The available options are “Password” (default) and “Certificate”. |
| Password
(If user authentication is selected Password) |
The password used for authenticating with the VPN server. |
| Certificate
(If user authentication is selected Certificate) |
All certificates uploaded at macOS > Security > Certificates are displayed here. Select one from the list. |
Proxy Server Settings
A proxy server secures a Mac from harmful external files and websites by acting as an intermediary between the device and the internet. All communication made between the device and the internet are made through the proxy server so harmful websites can be blocked. The available values are None, Manual and Automatic.
- None: This means no proxy is configured thus making the device vulnerable to threats.
- Manual: Set up the proxy configurations manually by providing the below details:
- Server: The server address of the proxy server (IP address).
- Port: The port number associated with the proxy server.
- Authentication: The username to get authenticated with the proxy server.
- Password: The password associated with the username provided above.
- Automatic: Set up the proxy automatically by providing the proxy server URL and the rest will be handled by Hexnode UEM. For example: http://proxy.acme.com.
Associate the policy with macOS devices
If the policy has not been saved,
- Navigate to Policy Targets > +Add Devices.
- Choose the target macOS devices and click OK. Click Save.
- You can also associate the policy with device groups, users, user groups or domains from the left pane of Policy Targets tab.
If the policy has been saved,
- Go to Policies and choose the desired policy.
- Click on Manage drop-down and select Associate Targets.
- Choose the target entities and click Associate.
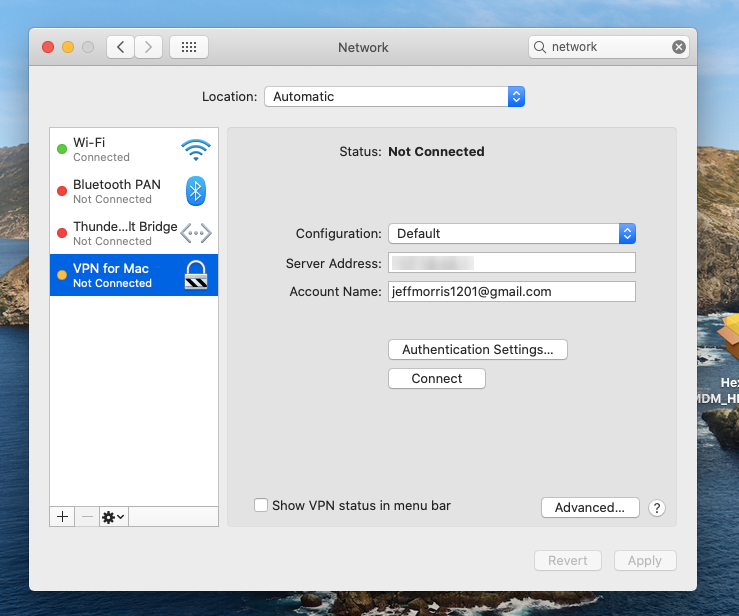
What happens at the device end?
On associating the VPN server configuration with the Apple device, users will be able to view the deployed VPN network configurations among the available networks (System Preferences > Network). They can manually connect to this VPN, if required.