What is a Kiosk Software?
Kiosk Software is the security software that locks down a device so that the user is restricted to activities in the scope of the software.

Get fresh insights, pro tips, and thought starters–only the best of posts for you.

Trust is something that has to be earned, be it in real life or in your enterprise architecture. Zero Trust is a security concept based on the principle that no device, user or application attempting access to your architecture can be considered secure. First coined in 2010 by John Kindervag, the term Zero Trust challenges the traditional security models that are based on the assumption that everything inside an organization’s network can be trusted. As such, legacy technologies such as VPN and NACs are used to verify the users outside the company network before granting access to the network. The older models assume that all users will behave responsibly and that their identities are never compromised. Zero Trust recognizes the vulnerability of this assumption. Instead of trusting anything inside or outside the organization’s perimeters, everything has to be verified before being granted access. For enterprises betting everything on securing their systems, Zero Trust is an unavoidable update for cybersecurity.
The traditional security models operate under the convenient assumption that all cyberattacks must occur due to outside forces. However, the reality is not so convenient. According to a report from Verizon, 34 percent of all security breaches were insider attacks. In comparison to external attacks, insider threats are often guaranteed to cost the company heavier losses. So the question arises: How to secure your organization completely?
The traditional security models classify the network into perimeters and sub-perimeters using specific rules. If an attack occurs, the spread of the attack is defined by the sub-perimeters. Such an approach can be faulty since the point of infiltration may differ from the target location. With the users accessing different apps from different types of devices from various locations, a simple and dynamic security model is required to adjust to the changing needs. Amongst the new security models, the Zero Trust Model is one of the most promising ones. Zero Trust completely erases any perimeters within the organization. By verifying each and every user/device/application/location, the organization gains granular visibility for all traffic, be it internal or external.
The success of the Zero Trust model is rooted in the transition from “trust, but verify” to “never trust, always verify” approach. So, what does implementing Zero Trust look like? There are five important components in building a basic zero trust architecture:
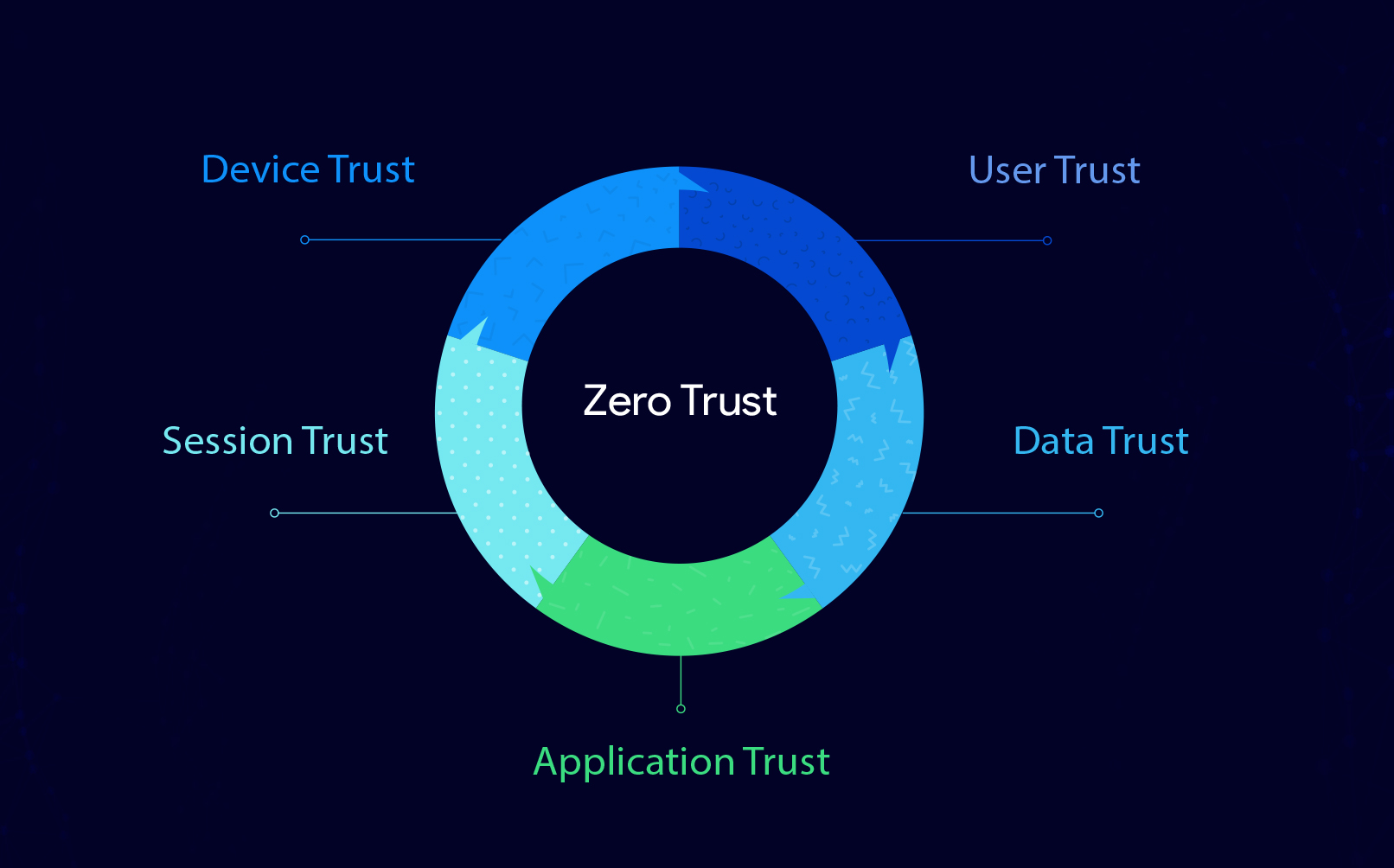
The first step in achieving Zero Trust security is to securely provision devices for users with a Unified Endpoint Management (UEM) solution. With Hexnode UEM, you can easily onboard your devices across iOS, Android, Windows, macOS and tvOS platforms using a variety of methods. Both BYOD and corporate devices can be enrolled over-the-air using services like Apple Business Manager or Android Zero Touch Enrollment. Provisioning the devices using a UEM solution gives the IT admin the control to assign the users to the corresponding devices, establishing both device and user trust.
An unsecured corporate network leaves many doors open to potential attackers who want to steal valuable data or customer information. To implement zero trust, we need to assume that the users are potential attackers. Hexnode allows you to set up and connect your devices to a secure Wi-Fi network without the user knowing its password. For additional security, you can also add a SCEP or PKCS certificate. You can also configure network usage rules for iOS devices and data usage restrictions for Android devices. Using features like Web Content filtering, you can restrict user access to trusted websites and decrease the surface area for hackers.
Zero trust model is based on adaptive access. The policies have to defined on the basis on full context, i.e., verifying the user and the device, configuring app permissions, securing the networks, and overall threat management should be monitored on a regular basis.
The IT admin can customize compliance rules and enforce it in different ways. For example, if the device is not application compliant due to missing apps, the admin can install the missing application from the Hexnode Web Console. If the device is lost or stolen, the admin can remotely wipe or lock the device to prevent the loss of any important data.
Which apps are trustworthy and which are not? All decisions are in the hands of the IT admin. The admin can blacklist/whitelist apps, configure app permissions and configurations, install and uninstall apps silently on supported devices, and design custom app stores. In addition, Hexnode provides work and personal app segregation.
Mobile devices are prone to data leakages and it is essential to protect the critical information. The threat management capability of Hexnode helps you to secure data rom network, app-based and physical threats.The admin can configure password policies to enforce strong passwords, configure restrictions that enforce encryption, and carry out full disk encryption of Windows with BitLocker and macOS with FileVault. The encryption ensures that the data is secured and the data integrity is maintained at all times.
For adaptive access, continuous monitoring is important. It is only possible with good reports that are up to date with the latest device and user information.
Trust is a vulnerability that can be exploited. The castle and moat mentality has become outdated as more and more organizations are moving towards zero trust. Now, with the Work From Home becoming increasingly normal, Zero Trust is the preferred model for addressing remote work security challenges. The very first step in achieving zero trust in your organization is to use a Unified Endpoint Solution to manage your devices. One of the major challenges that an IT admin faces while trying to implement a zero trust model is the different types of users, devices and applications. With Hexnode UEM, the process becomes simpler as the admin can easily manage everything from a single console.