We look forward to what Apple brings to the device management table every year at its midyear event: Worldwide User Conference (WWDC). Without a doubt, the “What’s new in managing Apple devices” session is one of the most exciting sessions that we anticipate, and Apple never disappoints. This time, we saw other detailed sessions on important device management features. One of these deep-dive sessions covered the new account-driven user enrollment. Apple is obsessed with security and we can see how it is reflected in their announcements this year.
User enrollment is a device management option for BYOD deployments, where the devices to be managed are owned by the user and not the organization. It helps to assure both the user and the organization that their respective data is secured.
- Three components of User-Enrollment
- Newly announced: Account-driven user enrollment
- 1. New way to access Managed Account in Settings
- 2. iCloud Drive for Managed Apple IDs
- 3. Remove managed app when a user-enrolled Mac computer disenrolls
- 4. Managed Pasteboard and Required App
- 5. An additional layer of security in user enrollment
- 6. Option to incorporate ongoing authentication
- Our say
Three components of User-Enrollment

- Managed Apple ID: Managed Apple IDs are owned by the organization. The organization should have an Apple Business Manager or Apple School Manager account. The Managed Apple IDs are used to provide access to the users to Apple services such as iCloud.
- Data Separation: At the time of enrollment, a separate container is created to store the managed apps, accounts and data. This secures the corporate data and helps to separate work and personal data.
- Management capabilities: The management capabilities should be limited to those who are authorized to do so. With User Enrollment, the admin has full control over the managed content but limited to no access to personal data and settings of the user. System-wide operations such as remote wipe are also unavailable to the MDM server, ensuring complete privacy and security for the users.
Newly announced: Account-driven user enrollment
1. New way to access Managed Account in Settings
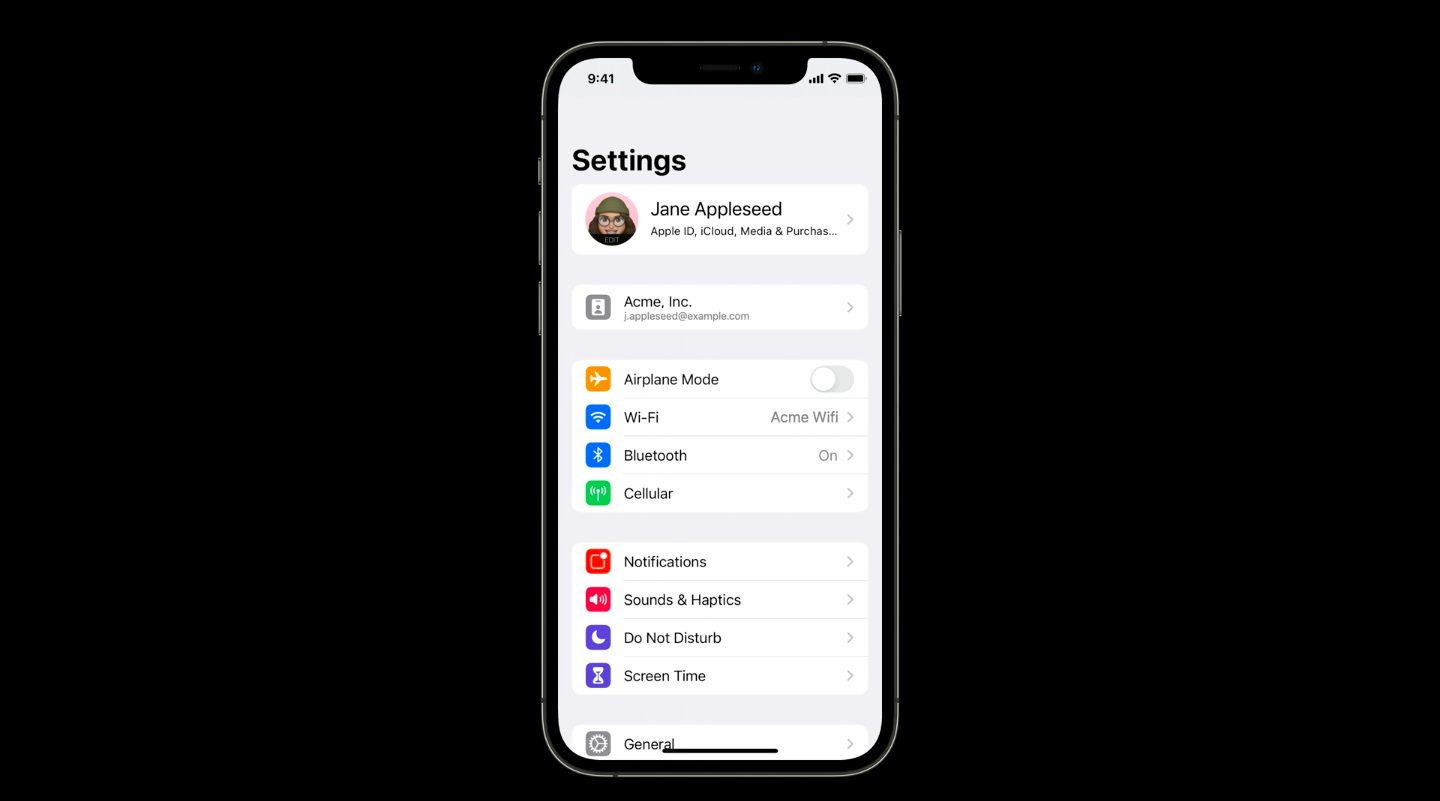
If the device user enrolled, the account will be displayed at the top of the device settings. The user can easily view the parts of the system that are managed by the organization and the parts that are not. This is an important feature as it clearly separates the organizational content from the personal data and accounts of the user in a visible manner.
2. iCloud Drive for Managed Apple IDs
Apple has announced that Managed Apple IDs will support iCloud Drive in iOS 15 and macOS Monterey. iCloud Drive would also follow the Managed Open-In restrictions for managed app and data access.
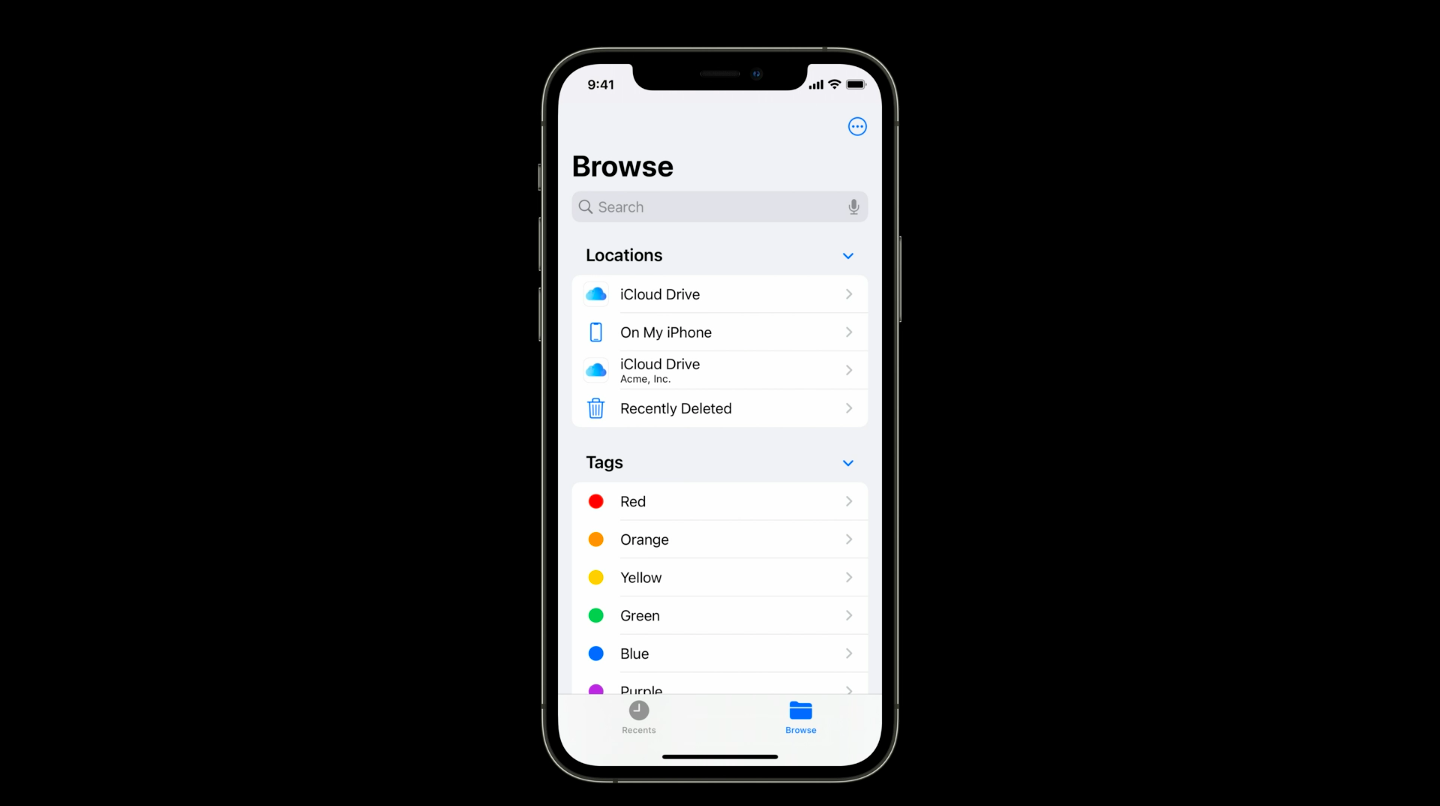
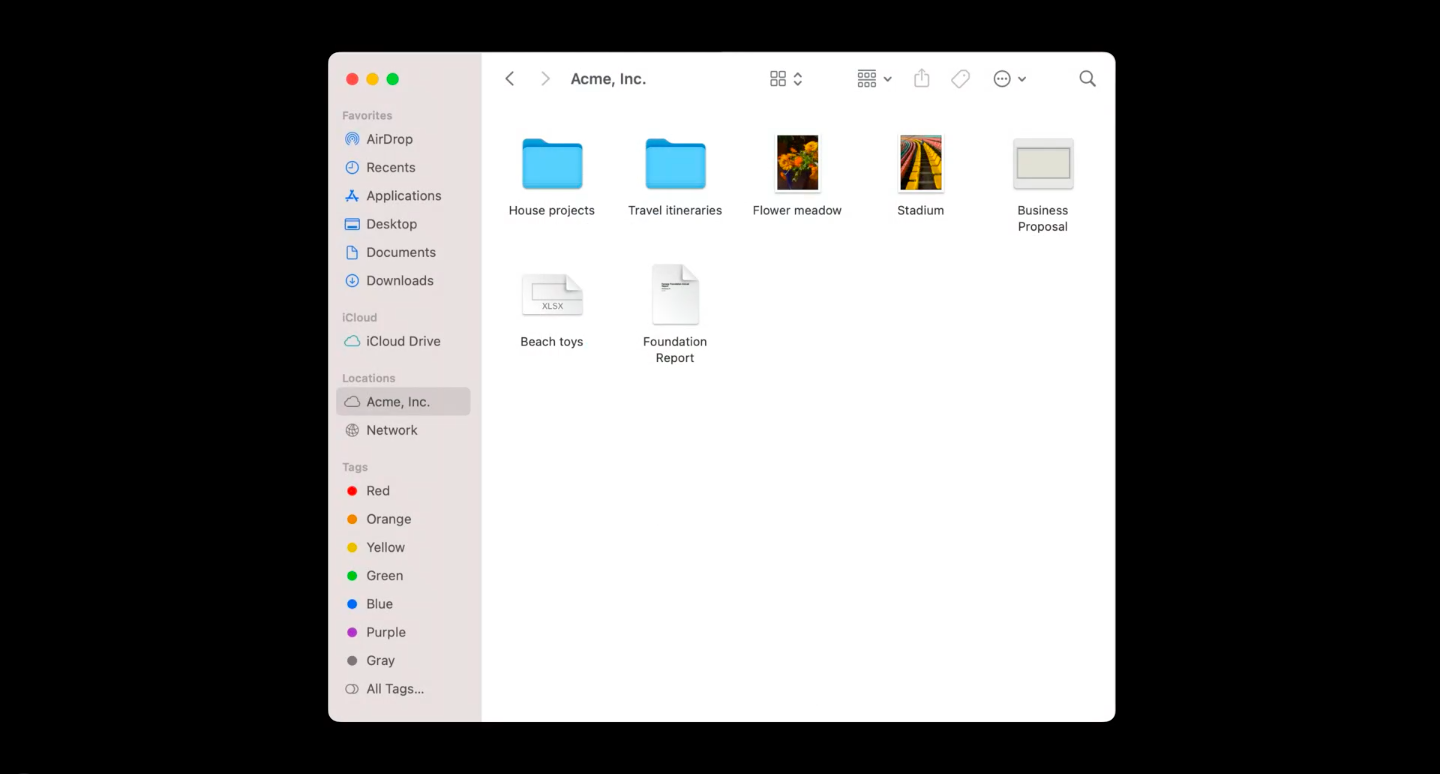
3. Remove managed app when a user-enrolled Mac computer disenrolls
In macOS Monterey, Macs enrolled with user enrollment would remove the managed apps with an MDM command or when the devices are disenrolled from the MDM. Just like in iOS, the managed app data is stored on a different volume.
4. Managed Pasteboard and Required App
Managed Open-In has now expanded to include Copy & Paste. Organizations can control the data being pasted across the managed and unmanaged apps. Apple has also introduced Required App for unsupervised devices which allows the admin to install one pre-approved app silently without prompting the user.
5. An additional layer of security in user enrollment
The onboarding for user enrollment in iOS devices used to be initiated and controlled by an MDM enrollment profile. The new user enrollment establishes the organization’s identity as the entry point. An additional layer of security is established during the enrollment flow. The MDM server can now verify the user even before the MDM profile is downloaded to the device. How does it work?
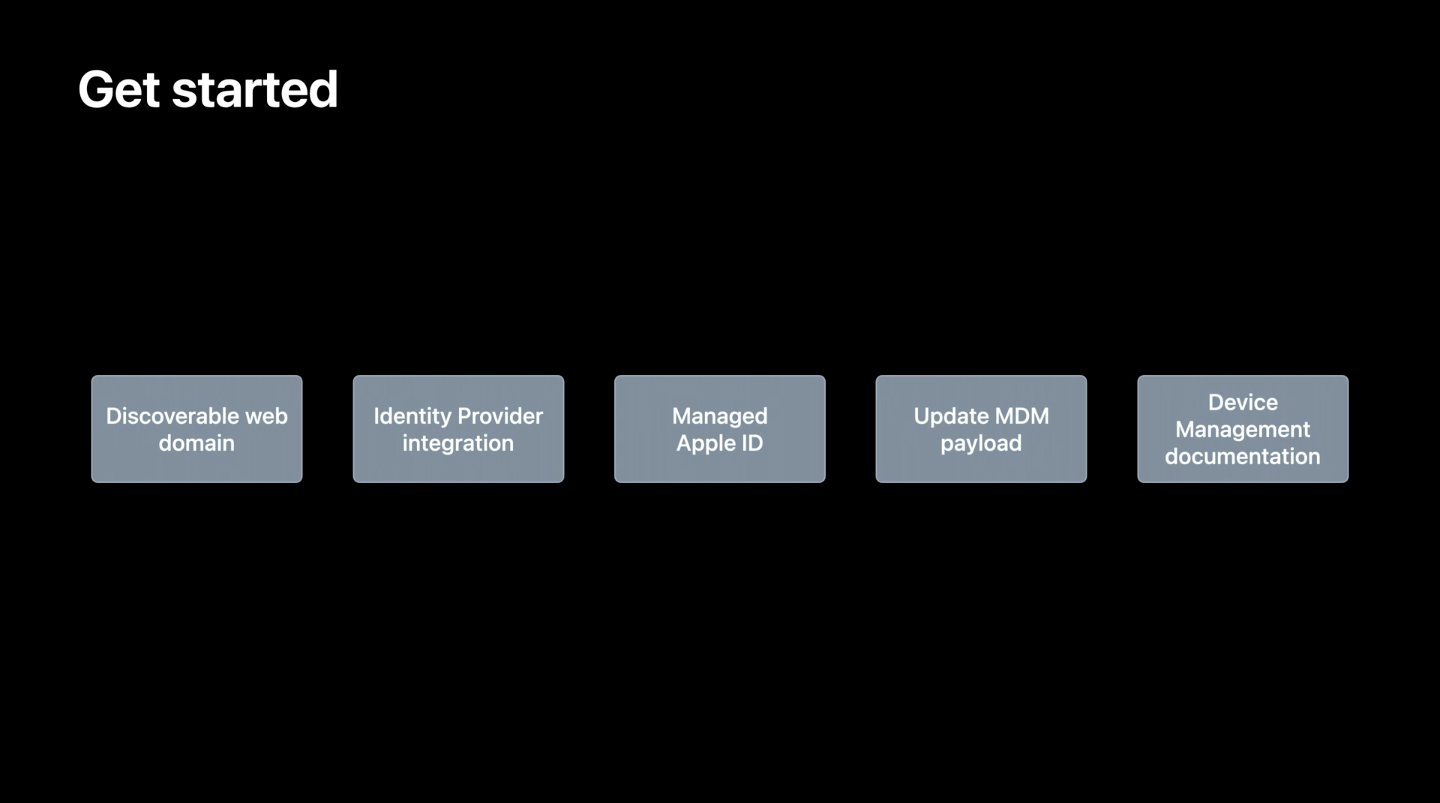
There are four core components in the new account-driven user enrollment onboarding flow:
- Service discovery – User identifies the organization’s MDM server.
- User authentication – Here, the MDM server validates the user.
- Issuing the session token – Ongoing authentication is performed by issuing the session token.
- Enrollment – The device finally gets enrolled by installing the MDM payload to the device.
The user goes to the new VPN and Device management section in the Settings and taps the new “Sign in to Work or School” button. There, the user has to enter their organizational ID which triggers the service discovery step. After the authentication, the assigned managed Apple ID is pre-populated in the next screen, where the user is expected to enter their password. After this authentication also succeeds, the user then allows the management of their device. The user then has to enter the device passcode to create a separate encrypted partition for enterprise data and to authorize the MDM enrollment. The device is enrolled in the MDM only after following all these steps.
6. Option to incorporate ongoing authentication
In the onboarding flow that we discussed above, the server authenticates the user before sending enrollment data. In iOS 15, Apple has also announced the option for organizations to re-authenticate the user at any point of time. MDM server can now validate authorization on every request from the client and ask the user to re-authenticate their identity credentials. If the user’s authentication attempt fails, the server may no longer trust the device. The MDM server can then remove any sensitive data or apps from the device or completely disenroll the device.
Our say
Bringing and using personal devices for work is always a cause of security concerns within an organization. However, with focused features and updates like account-driven user enrollment, it is definitely going to be easier for administrators to manage Apple devices in a BYOD environment. Apple has announced many great and revolutionary features for device management this year. Read WWDC 2021: What’s new in Apple Device Management to learn what else is in store for you.