Started way back in Android’s Lollipop stages, the Android Enterprise program has seen steady growth in its user base and features. Among these, one of the most important features was introduced in Oreo. The zero-touch Enrollment method.
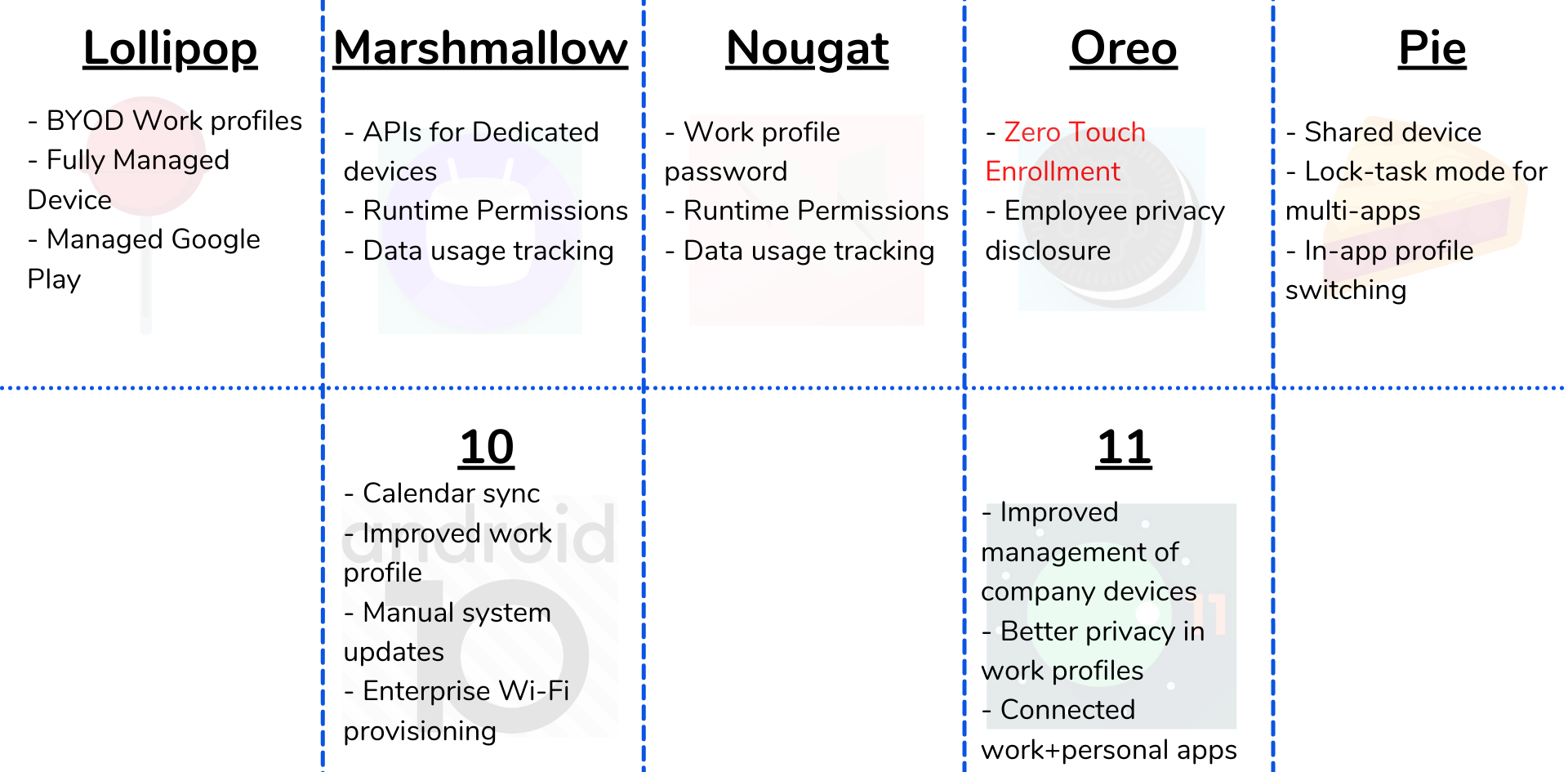
With the existence of various business models and organization structures, Google provided its users with various enrollment methods like NFC, QR code, DPC identifier, and G-Suite. Zero-touch is one among these and as Google argues, it’s the best. It provides simplicity and flexibility to the IT manager when it comes to device enrollment and management. There is no manual setup required, it simplifies the configuration process and it is a consistent enrollment method applicable across devices.
In November 2020, Google announced some changes that were going to be introduced into zero-touch enrollment. Most of these changes are groundbreaking and it improves the customer accessibility of zero-touch enrollment. Let’s delve in further.
Zero-touch in all 9.0 + devices.
One of the most common complaints that zero-touch users have had worldwide is regarding device availability. As of right now, zero-touch is optional which means that it is not available universally on all OEMs. It was delivered as an optional app the OEMs could take and include in their devices. This will not be the case anymore. Moving forward zero-touch will be featured as a part of Google Play Services and would thus be available universally across all Android devices running 9.0+.
This streamlines how you actually buy Android devices for your organization. Previously you had to go through a directory or catalog to find out the devices that were actually compatible with zero-touch. With the addition of this feature, there would be no more confusion regarding what device to choose from, because this would be available for all recent Android devices.
It is also a win for the OEMs who were a bit hesitant to add the zero-touch app to their devices due to the cost of integration. With this feature, Google has reduced the cost down to zero.
This feature is also backwards compatible I.e., you don’t need the latest version of Android to utilize this feature. It is a part of the Google Play services, it will be downloaded and updated dynamically when required during the device set up.
Samsung devices are now ZTE compatible
In conjuncture with the feature mentioned before, Samsung devices, with Android 9.0+, support both Knox Mobile Enrollment (KME) and zero-touch enrollment. This is essentially a new feature for Samsung devices. Even though KME does surpass zero-touch to a certain degree in a few areas, organizations that require enrollment from a central console will welcome this feature with open arms.
That’s not all though. It looks like Samsung Galaxy phones and tablets would soon be Android Enterprise Recommended. This is what David Stills, Managing Director of Android Enterprise had to say.
We are excited to welcome Samsung Galaxy smartphones and tablets to the Android Enterprise Recommended program building upon our longstanding partnership to deliver great mobile experiences to businesses.
Android Enterprise Recommended is a critical tool that helps enterprises analyze, evaluate, and choose devices that meet Google’s benchmarks regarding software, hardware, and updates. By adding Samsung to AER, Google has expanded the device choices that are available to you. This gives you more flexibility when it comes to selecting the devices for your organization. Also, Samsung being a major and one of the most trustworthy players in the mobile device market, it can urge more businesses to deploy mobile workforces.
Integrating your EMM and zero-touch
With this new feature, you can manage all your zero-touch accounts from a single pane of glass, your EMM solution. You no longer have to switch between the zero-touch portal and the EMM console, if your EMM solution includes the zero-touch iframe in their console. With this feature, zero-touch can now detect which EMM solution you are using. This means that zero-touch can now provide smart decisions and recommendations on basis of the EMM solution that you are using. Another plus side of this feature is that it streamlines the pushing of configurations onto a new device. Once both the accounts are linked configurations can be automatically created based on your EMM solution. Previously, pushing configurations or DPC extras was a very fiddly process with a JSON code. This method is now obsolete thanks to this new feature.
Changes to the Solutions Directory
To reflect the features mentioned above, Android Solutions Directory has also made some significant changes.
- The solutions directory only lists profiles of Android Enterprise Recommended devices, the filter used to show devices that were zero-touch ready has been removed.
- Information is now available about security update support in the device profiles which includes the end date of updates for the particular device and the frequency of security updates.
- New filters are added to help select the best device for your needs:
- Last date of security update support
- Security update frequency
- Additional certifications: ioXt, Common Criteria
- Knowledge worker devices
Some caveats
Competing Solutions
It would be interesting to see how Samsung would play this new integration. KME and zero-touch are two competing solutions. It would be interesting to see how they push both these enrollment methods. This can lead to quite a bit of confusion among the end-users. Because of the native deployment method, KME does provide a degree of flexibility and security that zero-touch cannot provide. But, zero-touch does provide versatility when it comes to device choices.
Device Vetting
Just because choice is abundant, doesn’t mean that the IT admin can slack on device vetting. Even though all Android 9.0+ devices should support zero-touch, there might still be OEMs who wouldn’t integrate it because it wouldn’t be technically feasible for them. So, even though zero-touch would be available to them, these devices would be plagued by other issues, like frequent crashes. It is always better to check the devices that are AER validated.
Conclusion
The Android Enterprise team brought forth two, as we said earlier, groundbreaking features. The universal availability of zero-touch is a boon for any organization that is just starting off in its device management journey. It has opened up a world of opportunities for SMBs because it is now easier than ever to go mobile. Talking about easiness, making device configuration easy with the zero-touch iframe is a masterstroke from the AE team. It reduces needless iterations as everything can be managed from a single pane of glass. These changes show that the AE team is listening to its community and bringing about changes that are asked by them. This is a very good sign for things to come and we personally can’t wait for what’s in store.






