The essential guide to establishing a mobile device policy
Learn how to develop a mobile device policy for your organization

Get fresh insights, pro tips, and thought starters–only the best of posts for you.
Alma Evans
May 10, 2019
9 min read

If you are not new to the mobility management space, you would have come across terms like MDM, EMM, UEM, etc. Knowing the difference between these management techniques is really important as it is necessary for you to identify the right solution to suit your organization’s needs. So, let’s see what each of them exactly means and offers.

Organizations now are more concerned about their employees working remotely to be productive around the clock. The need to proactively manage their laptops, smartphones, tablets, wearables, ruggedized devices, or even the Internet of Things (IoT) especially handling sensitive business data is critical than ever before. As the volume of proprietary information transferred across the endpoints for high level business operations is frequently growing, devices coming with some sort of predetermined security management and hardening are sure to bring more confidence and success to the enterprise.
Employing a strong mobility management strategy is often the first step towards preventing any data breach and can impact a range of outcomes. A secure, unified, comprehensive and future-proof mobility management tool can address most of the device management concerns to bridge all the security gaps and prevent users from circumventing any security systems in place. The ever-evolving mobility management technologies are always urging organizations to seek out better management options to ensure security without overburdening the user. As the mobility management landscape is in continuous flux, choosing the right solution is an important challenge that IT teams have ever encountered to remain agile and competitive in the marketplace.

Mobility management involves device deployment, configuration, monitoring, securing, and ongoing support. Several categories of mobility management tools are out there, and chances are there to get confused with the jumble of three-letter acronyms including MDM, EMM, and UEM. Knowing the difference between these management products is important to avoid the enforcement of a mobility management plan that is not the best fit for your organization. Deploying the wrong strategy can cost business money and kill employee morale. Here are a few pointers for those who are struggling with breaking down the difference between various types of mobility management tools that are available today.
Mobile Device Management (MDM) allows you to manage and secure corporate or employee-owned mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets deployed across multiple OS platforms. Enrolled devices can be configured to address company policies and requirements. Devices can be locked, tracked and monitored remotely from the MDM console.
Other major services that an MDM solution should offer include:
and so on.
In short, the main objective of MDM is to give organizations secured control over their devices.
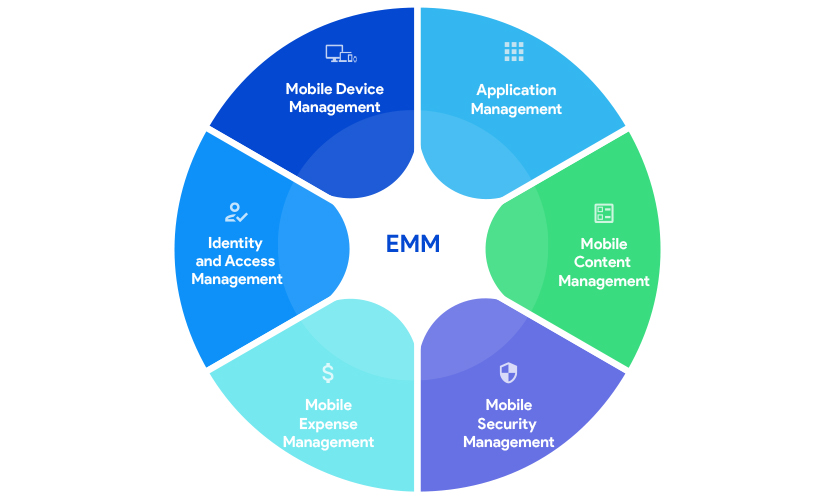
As MDM solutions functioned at the device level it became difficult to break through the challenges arose with BYOD (Bring Your Own Devices) and COPE (Corporate Owned Personally Enabled) trends in the organizations. Sensitive corporate data on employees’ devices had to be secured without compromising their privacy. So, MDM transformed into a more comprehensive solution, EMM.
Enterprise Mobility Management (EMM) encompasses technologies to manage apps and content with stringent security. Generally, EMM offers everything that MDM can perform. Other major components of EMM include:
Unified Endpoint Management (UEM) approach consolidates the management of all endpoints including smartphones, tablets, laptops, wearables, TVs and IoT devices providing a single pane to manage devices, apps, and data. It is an evolution and combination of MDM and EMM along with the capabilities of traditional client management tools. This centralized platform with a multi-device architecture covers all platforms, a wide range of devices as well as services and help you remove the hassle of complicated integrations among different tools on multiple platforms.
UEM solutions have all the capabilities of its predecessors including mobile device management, mobile application management, mobile security management, mobile content management, mobile expense management, kiosk management and so on. Taking management a few steps further it offers other enhanced features like no-touch deployment of devices under different platforms to make them business-ready over-the-air. It has seamless business integrations to boost productivity and can manage any of the business scenarios: BYOD (Bring Your Own Device), CYOD (Choose Your Own Device), COPE (Corporate Owned Personally Enabled) or COBO (Corporate Owned Business Only).

Without a few points in mind, making the right decision on the most suited mobility management tools can be next to impossible. Here are the key considerations for decision making:
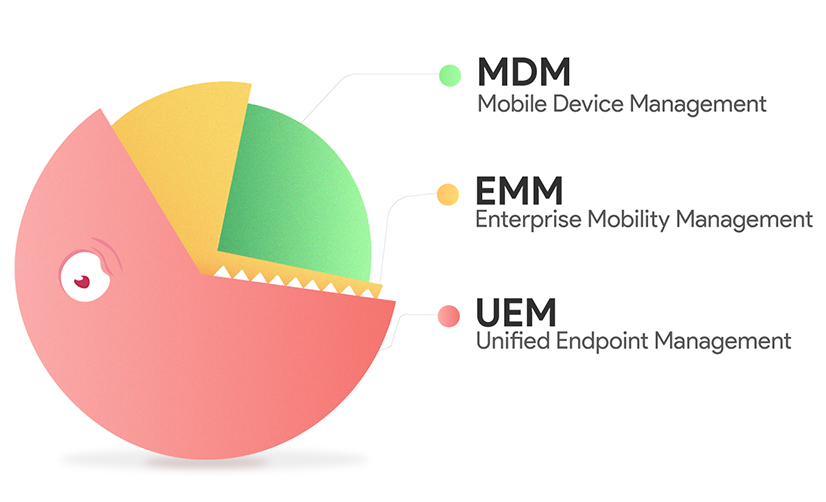
So, to sum up, MDM, EMM, and UEM are the different evolutionary stages of mobility management and addresses the security and privacy concerns raised as a part of the modern business trends. Simply put, the main difference between these solutions lie in their management scopes. MDM focusses on the basic management of mobile devices by leveraging device-level policies and putting security protocols to provision these devices. EMM is a much comprehensive approach that includes all aspects of managing enterprise mobility including MAM, MCM, MSM, MEM, Identity and Access management along with MDM. And finally, UEM implies a coherent mechanism to integrate the management of all endpoints along with mobile devices into a single platform.
After knowing the lines of difference between these management tools, it is quite easy to determine the right solution for your mobility needs. The point is to analyze, identify, and figure out your organization’s needs and choose the one that’s best suited for you.
No matter which mobility management strategy is right for you, Hexnode can help you with that!