The cyber world is changing, and it is crucial than ever to proactively protect yourselves from prying eyes. The technology-driven digitalization, proliferation of endpoints, and more remote access to data in this competitive world equal increased opportunities for tech-savvy attackers. Though identity theft is one of the oldest crimes, the attacking tools are becoming more sophisticated, and the attackers are out in force, enjoying an easy time stealing personal data. Attackers can effortlessly exploit endpoint vulnerabilities with new skimming technologies that can penetrate through the device’s window of exposure. The attacking methods used by criminals are plentiful, and they continue to evolve, making identity theft one of the fastest growing crime problem.
Untangling the mess from identity theft can be very challenging, and it can be difficult to spot early warning signs. Fraudsters take advantage of businesses as well as individuals. For corporations, remediating the problem can be a long and expensive task. So, it is vital to stay cautious of proposed identity thefts, and your vigilance starts with educating yourself on the most prevalent ways identity thieves get hold of your data. There are no ways to immunize yourself against identity theft completely. All you can do is to be well equipped to shield your personal data, know what identity thieves can do with your personal data and act swiftly if someone manages to thieve it.
What is meant by identity theft?
Identity theft is an offensive process that involves stealing the personal or financial information of an individual unwittingly, which is later used for fraudulent purposes. Usually, any Personally Identifiable Information that can be used to access a person’s financial resources like an individual’s name, date of birth, address, bank account number, credit card number, social security number, medical insurance account number, electronic signature, fingerprint, driver’s license number, passport number, PINs, and passwords can be compromised in identity theft. Identity theft is a very serious crime, and it can happen to anyone.
Identity thieves deliberately use the stolen identity for credits, merchandise, or financial gains in the name of other persons, and the victims sometimes might suffer adverse consequences that will rapidly spiral out of control as they are unknowingly held responsible for the perpetrator’s activities. The victim’s creditworthiness, reputation, and data privacy will be damaged due to any transactions or purchases made by the imposter, which costs them a massive sum of money, effort, and emotional distress. The thieves may sometimes provide the contents to a crime ring. It may take a single day to several months or years accompanied by constant investigations and long-term assistance to tie over the consequences.
How identity theft occurs?
Identity theft is committed in various ways. Due to the nature of the technologies used for identity theft, personal information is at risk anytime. Criminals are increasingly using computer technologies and becoming more creative in how they steal your identity. Understanding how identity theft occurs helps you better stay vigilant and identify what kind of data is to be protected. The techniques used range from mere shoulder surfing to high-end social engineering methods used to access corporate databases.
Identity theft methods:
- Shoulder surfing – Thieves discreetly gleans information when people fill out personal information on forms and peer over their shoulder when typing sensitive information like passwords on a keypad, credit card number on a phone or computer, and entering ATM PIN. They may also listen to the victim’s calls to steal their personal information. This usually occurs in crowded public places where observing others is comparatively easy.
- Mail theft – Thieves directly sift through the victim’s mailbox to access junk mails containing credit card bills, bank statements with the account number, tax form with a security number, or other documents containing personal information. Digging through trash mails to find receipts containing personal information is a very early method used for identity theft since long before the advent of the internet. Bank statements and credit card information sent through post can also be vulnerable to theft. Information can even be stolen from computer based public records.
- Malware – Malware or malicious software can be designed to steal essential data from the device on which it is installed or spy over the user’s online activities to steal their personal information. Malware like viruses, trojans, spyware, or keyloggers are commonly used for this, and they find open doors for the thieves to get their hands on the data residing on the system. Criminals sometimes hack devices in a network to access systems and databases to obtain personal information in bulk.
- Phishing – Phishing is a process where scammers use deceptive emails to trick people and steal sensitive information. Different forms of malware come attached to phishing emails, and sometimes links to fraudulent or spoof websites will also be attached where users are prompted to type in their personal information. Sometimes the victim will be tricked to fill a data collection form wherein their important personal information is disclosed. Phishing emails typically look like a legitimate one from a reputed source so that people easily fall victim. Rarely, the fishy email may contain spelling or grammatical mistakes, seems coming from unofficial email id, and include an urgent request. So, it isn’t easy to find them out. Scammers also use SMS text messages, phone calls, or other forms of electronic communication other than stealing or diverting mails to impersonate trusted organizations.
- Phone scams – Identity thieves directly make a call pretending that they are from a bank or other reputed firms and prompt users to share their bank account details and other personal information.
- Dumpster diving – Thieves sometimes sifts through garbage cans to get useful information. Retrieving people’s discarded file documents from trash dumpsters is an easy method used for identity theft. Pre-approved credit cards are often thrown unopened to garbage without proper shredding, which opens up an opportunity for credit card theft. Discarded checks, health insurance cards, and tax-related documents are other vital data that are accessed by rummaging through the rubbish.
- Wi-Fi hacking – Public Wi-Fi doesn’t properly encrypt the data flowing through it. So, having the Wi-Fi password with them, criminals can easily snoop on data traveling to and from other’s devices and intercept the personal information which people send through a public Wi-Fi network. Criminals sometimes create their own fake Wi-Fi hotspots in public places to attract people to use it and thereby easily get access to their devices. In other cases, attackers use different tools to hack other private Wi-Fi networks that are unencrypted and don’t have a VPN in use to stole data.
- Skimming – Skimming devices are placed over an ATM or card readers at a point-of-sale. Here the actual card reader is replaced by a counterfeit device that captures the data contained in the magnetic strips of debit cards or credit cards and shares them with the fraudsters. Sometimes a small camera will be attached to capture ATM PINs and ZIP codes.
- Card information cloning – The card readers copy the information contained in the magnetic strip of a debit or credit card and use a counterfeit card with the same details to make payments.
- Direct stealing – Identity thieves grab and go valuable data typically by pickpocketing or housebreaking. For instance, they may steal misplaced cheques to obtain bank code and account number.
- Insider theft – Insider job of identity theft in the workplace is a common challenge for organizations handling the personal information of their customers. Dishonest employees who have access to the database may intentionally steal customer data to hand it over to other fraudsters or sell it in the dark web marketplace.
- Data breach – Data breach is a steadily growing crime, and a portion of the data breach victims have their identities stolen as well. When some unauthorized ones gain access to a corporate’s sensitive data, customer data is one of the valuable information that could be easily stolen.
Get to know the warning signs for identity theft
It’s really frustrating that identity theft can remain unnoticed for a long time as thieves are clever and cunning in their operations. However, it is important to spot potential frauds before it becomes a major threat. Here are some warning signs which indicates that the identity has been stolen:
- Unknowing withdrawals from bank accounts
- Impacted credit score and inexplicable denial of credit in spite of having high credit rates
- Not receiving bills or other important emails containing sensitive data
- Receiving bills or payment reports for unknowing accounts
- Fake accounts and false charges on the credit report
- Rejection of health plans due to unknown reasons
- Unusual IRS notifications that multiple tax returns are filed under a person’s name or income data from an unknown employer
- A data breach on a company that stores the victim’s personal information
- Getting bills for strange purchases or credit card statements for unknowing sign ups
- Unauthorized bank transactions
- Denial of electronic tax filing
- Receiving authentication texts and emails from unknown accounts
- Getting bills for unrecognized healthcare benefits
- Getting unnecessary calls from debt collectors for overdue
- Job opportunities unexpectedly fall through after the prospective employer runs a credit check
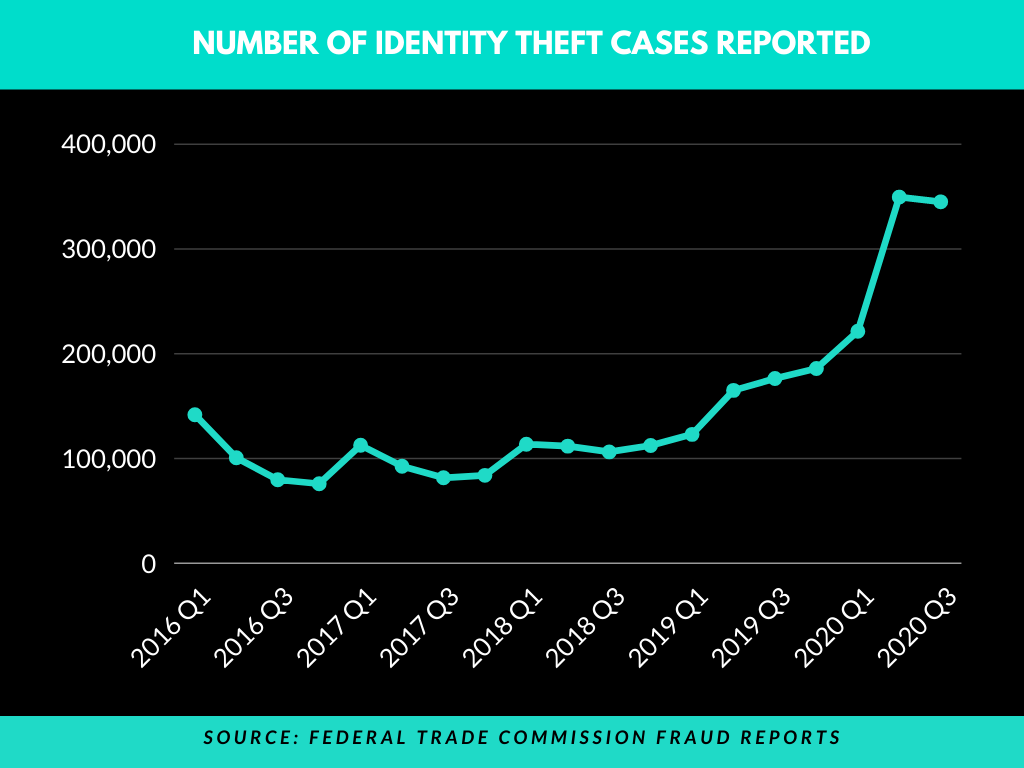
Some recent statistics
Fraud Reports by Federal Trade Commission Customer Sentinel Network clearly shows a steady increase in the rate of identity theft in recent years.
Here is a quick overview of the identity thefts reported by subtype
| Theft subtype | 2019 Q4 | 2020 Q1 | 2020 Q2 | 2020 Q3 |
| Debit card, Electronic funds transfer, or ACH | 6374 | 6832 | 8191 | 7660 |
| Employment or wage-related fraud | 4011 | 6158 | 7534 | 6714 |
| Tax fraud | 3006 | 12519 | 39295 | 22326 |
| Email or social media | 2844 | 3029 | 3681 | 3800 |
| Insurance | 1404 | 1865 | 2473 | 2247 |
| Medical services | 8280 | 9699 | 12983 | 12335 |
| Online shopping or payment account | 3028 | 3343 | 3969 | 3903 |
Different types of identity theft
Identity theft is a broad term which involves various forms, the most common among which are listed below:
- True-name identity theft – Fraudsters steal other person’s data and open new accounts or services in their name. They may establish a new cellular phone service, start a new credit card account, or open a new banking account to get blank checks.
- Account takeover identity theft – Fraudsters gain access to the victim’s existing account by means of the stolen identities. Once they get access to the victim’s account, they change the email address associated with it and make all transactions before the victim realizes the threat.
- Criminal identity theft – Fraudsters commit crimes and provide stolen identities to the police when they get arrested for disguising themselves as another individual. Criminals either submit government issued identity documents or a fake ID to prove themselves as the other individual. So, in police records, the identity theft victim will be charged, letting the actual culprit off the hook. Criminal identity theft can sometimes have a long-lasting effect that even when the victim can somehow manage to prove his innocence before the police and judiciary, they may encounter problems due to bad background in the future as some data aggregators may still have false criminal records in the victim’s name.
- Medical identity theft – Fraudsters steal medical information like health insurance information for receiving medical services or prescription drugs or to get access to the medical records of other people. All the fake details will be added to the victim’s account and the health insurance provider of the victim may receive unknown bills.
- Tax identity theft – Fraudsters files a tax return in someone else’s identity and nabs the refund, which is directly deposited to a bank account controlled by the thief. It is done by using the person’s name, address, and social security number. The victim may not know until they try to file a tax return.
- Social identity theft – Fraudsters use social media platforms for identity theft. They may befriend people in social media platforms and tricks them into sharing their personal information. Sometimes, the thieves go to the next level by creating a phony account in the name of other people and committing all the fraudulent activities from that account so that the victim will be blamed for any consequences.
- Child identity theft – Child identity theft is a form of identity theft that often remains unnoticed for a long time. Imposters steal minor’s identity, including social security numbers, when they do not have any data associated with them. Children’s information is misused to apply for bank accounts, establish a line of credit, receive government benefits, and take out loans.
- Senior identity theft – Senior identity theft is a form of identity theft that targets people over the age of 60. Senior may be unaware of the evolving techniques used by criminals and hence easily fall victim to such kind of attacks. To add, seniors are more likely to be in contact with medical care and health insurance units who stores a large amount of personal and financial information which makes them an attractive target for identity theft.
- Synthetic identity theft – In synthetic identity theft, fraudsters fabricate a new fake identity sometimes by combining the personally identifiable information of multiple identities which makes it the most difficult form of identity theft to track. This type of identity theft is more common in recent days, and the method may involve partial or complete fabrication.
- Financial identity theft – Any form of identity theft involves financial gains, and financial identity theft can be said a part of any other identity theft attempts. Financial theft is when the stolen identity is solely used for monetary gains like payment fraud, credit card fraud, new bank account openings, taking loans, and getting goods and services claiming to be someone else.
Impacts of identity theft
Identity thieves can benefit from personal information in a variety of ways. Though businesses are far more tempting targets for identity thefts than independent individuals, both individuals as well as businesses are equally likely to have harming repercussions following identity theft. Identity theft can brought in immediate financial loss or gradual damage to the credit status of the victim depending on the type of the data stolen and the way by which the thieves utilizes the stolen data. Technology has exacerbated the identity theft problem that only a victim could understand how devasting the effect can be both economically and emotionally.
Some serious aftereffects of identity theft:
- Criminals use stolen employee identification numbers to submit false income and withholding documents to get refunds.
- In the first place, victims probably get little to no assistance from the authority which has issued the identity document.
- There are so many identity fraud cases reporting that it is less likely to get immediate investigation assistance from law enforcement.
- In order to prove their innocence to the authorities, victims may often have to show the police report.
- Flagging the credit report for fraud may not always stop fraudsters from obtaining more credit.
- Victims must deal with abusive collection agencies.
- Businesses have to spend a significant amount of time cleaning up the mess from identity theft.
- Individuals, as well as organizations, suffer huge financial loses.
- Sometimes the thief may commit a crime in the victim’s name and the entire burden of those crimes falls on the shoulders of the victim.
- Attackers purchase items, spend money from the victim’s account, and even steal the superannuation of employees.
- Thieves may change the victim’s password and contact information for accounts, making the victims unable to recover their account.
- Stolen information sometimes ends up on the dark web, which makes the situation even worse.
- Attackers access the victim’s social media accounts to target their family and friends for the next session.
- Identity thieves take out the victim’s phone plans and other contracts.
Identity theft protection
The public often learns of a problem only when they spot the worst. Lack of proper cyber hygiene is a major cause for most of the high-profile identity theft cases. A proactive, defense-in-depth security approach in place is the key to protect yourself from the all-too-common occurrence of identity theft and to mitigate the risks caused by it. Here is a compiled list of some of the most effective countermeasures that individuals, as well as organizations alike, can adopt to defend a possible identity theft:
- Businesses should use an identity and access management solution
Whether you are a big, small, or medium-sized organization, adopting an IAM (Identity and Access Management) solution is vital than any other well-known security practices to prevent the identified vulnerabilities and exposure. Identity and access management offers tools and policies to manage identities and control user access within an organization. This ensures that only authorized users within the organization are accessing sensitive data.
Most IAM solutions offer role-based access control with additional authentication options like single-sign-on and multi-factor or two-factor authentication. IAM also involves basic security etiquettes like enforcement of password and maintaining proper password hygiene, mandating the use of VPN, data encryption, compliance checks, virtual containerization of work data, and remote monitoring.
With the use of IAM, organizations can eliminate the instances of identity theft by preventing the spread of compromised login credentials and avoiding malicious entry to the organization network. The best option is to go with a UEM (Unified Endpoint Management) solution that offers a harmonized set of security services apart from the identity and access management, which altogether can employ a multi-layer threat defense. - Monitor credit activity and financial statements
Many banks offer continuous credit card monitoring for its customers. Customers should take advantage of this and bank statements should be scanned for purchases that seem unusual. - Nurture and practice good cybersecurity hygiene
Think before responding to emails from unfamiliar sources and be on alert while opening email attachments. Never share personal information to unauthorized websites. Use only secure websites. - Shred important documents
Dumped hard copies of documents are the most underrated attack vector used by identity thieves. Be sure to shred all the important identity documents once you discard them after use. - Be cautious on social media
Always set social media account to private. Be extremely careful when making new friends on social media platforms and be wary of the personal data you share there. - Avoid carrying Social Security Card around
- Avoid the use of public Wi-Fi, especially while making online transactions. Avoid sharing sensitive information online if possible.
- Wipe all personal information or make the hard drive unreadable before dispensing old computer and mobile devices.
- Check state and national criminal databases to confirm you don’t have any unknown criminal cases reported in your name.
- Keep photocopies of credit cards, debit cards, and all other personal information so that even if they are stolen, you’ll have all the data readily available.
- Organizations should provide awareness to employees to easily identify threat patterns and practices.
If you suspect or are particularly worried about identify theft, immediately freeze your accounts, change your passwords, and report it to the authorities. Organizations should red-flag to let the customers know that their data has been compromised.