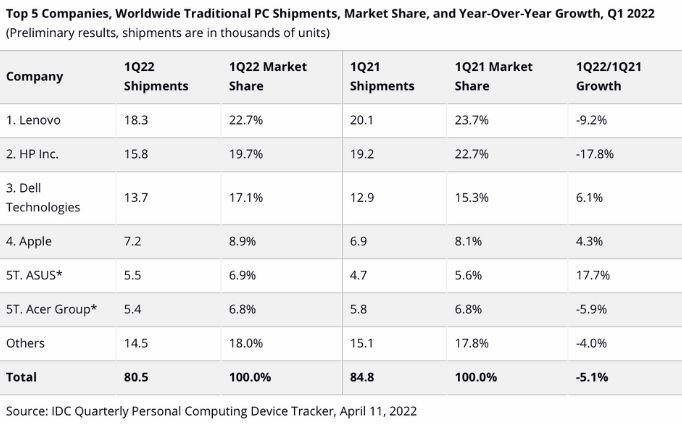
Windows has long dominated the enterprise landscape. The systems were easily affordable and it provided business users with an arsenal of tools they needed to work efficiently individually and as a team. However, recent stats suggest otherwise. Various Apple devices, Macs in particular are quickly foraging their way into the workplace. According to a recent IDC report, Apple shipped 7.2 million Macs during the first quarter of 2022, contributing to 8.1% of the market share.
Thanks to the amount of time users spend online, the internet has now become a minefield of personally identifiable data. The need to conserve user privacy has been around for quite some time with the passing of the data protection act in 1998 and HIPAA in 1996. This paved the way for the birth of several other compliance regulations and it was soon expected of OS vendors to start implementing features within their particular software to safeguard the privacy of users by enabling various settings to make the systems more secure and protected.

- Featured resource
- What you need to know about enhancing security and privacy in Mac
- 13 ways UEM helps in enhancing security and privacy in business Macs
- 1. Set complex password requirements
- 2. Remotely deploy restrictions to strengthen device security
- 3. Blacklist applications not approved by your organization
- 4. Define app configurations
- 5. Configure network and email settings to enhance privacy
- 6. Configure privacy preferences
- 7. Push security certificates remotely
- 8. Remotely push OS updates
- 9. Set time limits
- 10. Authenticate users via smart cards
- 11. Enable FileVault to ensure data security
- 12. Ensure the safekeeping of lost devices
- 13. Remotely push custom scripts
- Bottomline
- The easier way to manage your Mac devices
Featured resource
A Complete Guide to Mac Device Management
What are your pain points when it comes to managing Macs within your organization? How does UEM help in ensuring the privacy and security of users stay intact? Read this whitepaper to know how.
Download whitepaperWhat you need to know about enhancing security and privacy in Mac
Apple has over the years improved its security and privacy features in Mac devices with each iterations of the macOS software. Though the software has always carried the reputation of being impenetrable to various malware and ransomware threats, recent attacks where Macs were an easy target tell a different story. Some of the most notable Mac malware include Silver Sparrow, XLoader, XCSSET and Log4Shell. Mac continues to improve its in-built security features to identify and ward of these malware threats.
Apple implements a three-tiered defense approach to prevent the launching of any malware and remediating the malware if it is detected within the system. The first layer aims at stopping the malware from launching. This is done by the App Store, Gatekeeper and Notarization. If a malware is somehow able to penetrate to the systems, it will be blocked immediately.
The second layer blocks the malware from running on the systems. Tools like Gatekeeper, Notarization and XProtect are used to identify and block the spotted malware. This layer stops the malware from impacting the systems even further. XProtect rectifies malware that has successfully managed to execute. It is a built-in antivirus feature that uses signature-based detection to remove the malware. Apple updates this regularly to quickly spot new infections. When a known malware is detected, the software will be blocked, and the user will be notified and provided with the option to delete the software.
| Software Version | Features Introduced |
| Mac OS X 10.4 (Tiger) |
|
| Mac OS X 10.5 (Leopard) |
|
| Mac OS X 10.6 (Snow Leopard) |
|
| OS X 10.7 (Lion) |
|
| OS X 10.8 (Mountain Lion) |
|
| OS X 10.9 (Mavericks) |
|
| OS X 10.10 (Yosemite) |
|
| OS X 10.11 (El Capitan) |
|
| OS X 10.12 (Sierra) |
|
| OS X 10.13 (High Sierra) |
|
| OS X 10.14 (Mojave) |
|
| OS X 10.15 (Catalina) |
|
| OS X 11 (Big Sur) |
|
| OS X 12 (Monterey) |
|
| OS X 13 (Ventura) – Upcoming: Fall of 2022 |
|
13 ways UEM helps in enhancing security and privacy in business Macs
Data minimization, on-device intelligence, security and transparency are the four principles on which Apple bases its privacy policies. A UEM tool provides a centralized platform where admins can efficiently manage devices, monitor the flow of data and sensitive files on devices and generate real time reports regarding how compliant the managed devices and users are to the business requirements and policies of your organization.
1. Set complex password requirements

Weak passwords are often the leading cause of data breaches. The process of securing passwords and other credentials is an ongoing one that requires users to continually upgrade its complexity to ensure hackers are not able to easily penetrate corporate networks. Organizations can remotely define their password requirements through the UEM tool and restrict users from using the same password repeatedly. The Mac devices can be auto locked after a set time period of inactivity to minimize unauthorized access to sensitive information.
2. Remotely deploy restrictions to strengthen device security
In order to ensure data privacy, your business would have to incorporate certain requirements that are mandated by either privacy laws specific to your geographical region or regulatory compliances applicable to the industry your business operates under. You team can ensure these requirements are met by disabling various settings within the device functionalities, applications and the user’s iCloud accounts.
Apple has increased its privacy features with each version of its macOS software. Thus, Safari can now help users by recommending stronger passwords and auto-filling them to save users from remembering a long list of complicated passwords. This may not be a safe option all the time especially for enterprise users. Various privacy settings built-in within the user’s Mac devices can be disabled from the UEM console such as passcode modification, auto filling passwords and requesting passwords from nearby devices.
3. Blacklist applications not approved by your organization
You may want to restrict the use of some applications either because they hinder the productivity of your staff or have the reputation of mining data for unauthorized purposes. You can make a list of those applications and blacklist it to make sure users don’t have it installed within their devices.
4. Define app configurations
Although Apple has introduced a number of security features to restrict applications from collecting data from users, organizations can add in an extra layer of protection of their own by pre-configuring the application settings before deploying it to users. This ensures applications always function in line with your organization’s policies.
5. Configure network and email settings to enhance privacy
It’s easy to manually set up the network configurations if the total device count is low. The higher the device count, the harder it’s going to be to get it done manually. UEM helps automate this routine task by allowing admins to configure the network settings of a large number of devices via a policy where devices can automatically connect to your corporate network remotely without requiring users to enter a password. You can also define the network security type and configure the email settings to ensure users stay clear of any malicious mail or avoid being the targets of any phishing attacks.
The internet provides a wealth of information right at our fingertips. Unfortunately, they can also be a great hideout for many malicious actors and other lurkers waiting to steal sensitive information for financial gain. Your users may be quick enough to spot websites that look fishy right away, but it may require a lot more expertise to root out the cleverly disguised ones. Web content filtering is a great way to block access to websites your organization deems to be untrustworthy. You may want to explain the reasons for blocking access to a particular site to your staff to save some confusion later on.
With data thefts rising at alarming levels, it is always a safer option to enable a firewall within your enterprise Macs. In addition to preventing hackers from penetrating into your network, a firewall can keep a tab of your network activity and boosts the privacy of users by storing data in a secure and protected environment.
6. Configure privacy preferences

Certain apps and processes may require access to sensitive files in order to function. These require approval from users. Imagine users being disturbed during an important meeting to grant access to such requests. With UEM, these prompts can be automatically enabled by configuring the Privacy Preferences Policy Control (PPPC) profile. It also provides admins the ease with which various settings within the Privacy tab under System Preferences can be enabled remotely. The PPPC profile can also be used to deny permission to specific applications.
7. Push security certificates remotely
Security certificates is a more secure way for enterprise users to have access to corporate resources. This ensures sensitive information are shared only to users who have been authorized to access them with prior approval from their managers. These certificates can be installed and easily distributed among the devices via the UEM console.
8. Remotely push OS updates
Manage OS updates without disrupting the workflow of your users. You could either choose the option to install the update at a scheduled time or notify users of the upcoming update.
9. Set time limits
Sometimes implementing low key measures such as setting time limits in which users can access their business Macs can make a huge difference with regards to the safekeeping of corporate data and other digital assets. You can restrict users from accessing their device after a specified time period to curb the risk of connecting to insecure networks and other security issues that may arise when employees access sensitive files outside of working hours without adequate supervision.
10. Authenticate users via smart cards
Smart cards can be a smart way to authenticate users. The authenticity of users is checked with the help of a physical card where the user is required to enter a smart card PIN to login to their device. Various settings such as verifying the certificate trust and permitting the use of one card per user can be remotely configured.
11. Enable FileVault to ensure data security

Remotely enable FileVault to ensure complete protection of your corporate resources. FileVault is a full disk encryption tool that protects sensitive files from unauthorized access with the help of a full disk XTS-AES-128 encryption and a 256-bit key. Multiple regulatory compliances recommend deploying data encryption as encryption tools such as FileVault encrypts all the existing files and any new files users create within the device.
12. Ensure the safekeeping of lost devices
A lost device is never fully lost as long as it is managed by a reliable UEM provider. Admins can initiate a remote lock and wipe all sensitive content from the device as soon as it goes missing. You can track the location of the device in real time and get periodic updates on where the device is located until it is returned to the owner.
Long time users of Apple would be well familiar with the Activation lock feature. It guards the device from unauthorized access by ensuring the device can be unlocked only by entering the user’s Apple ID and password. Although, these measures are adapted to enhance security and privacy, they can be cumbersome especially when you need to reallocate the device to a new user but are not sure of the credentials of the previous user. You can bypass the activation lock in such cases.
13. Remotely push custom scripts
You may not find all the privacy and security functionalities you need within the UEM console, but you can still secure the managed Mac devices according to your organization needs by remotely deploying customs scripts from the UEM console. Scripts consists of a series of commands in a file which admins can execute to automate a series of routine tasks.
Bottomline
The best way to ensure complete security of business Macs is to monitor them on an around-the-clock basis. Keep a constant lookout for malware and other threats that could compromise all the data stored within the devices. Data breaches and information security incidents often occur when attacks are least expected. It’s always a good idea to keep a backup of all critical files and services to ensure the continuity of your business operations is not affected when these attacks occur.
The easier way to manage your Mac devices
Scale up your device management strategies by bringing onboard a UEM solution. Try Hexnode free for 14 days.
Sign up




